In the past year astronomers have discovered a dwarf “galaxy Ghost” that orbit our milky Way and called Antila 2. A new study by scientists from the University of Rochester suggests that this galaxy long time ago collided with ours, and the consequences of this collision are observed so far. Galaxy hit the edge of our milky Way, stolichnov it so that our galaxy was still shaking. The results of the study accepted for publication in the journal Astrophysical Journal Letters.

Our prospects understand the true size and shape of our galaxy is difficult. In General, scientists know that the milky Way has a disk shape with convex center (called a jumper). If you look at it from above, you can see its spiral arms, composed of bright stars and gas, leaving the center and crossing the galaxy in the middle.
The consequences of an intergalactic collision?
About a decade ago, it was determined that the matter of our galaxy is covered in “waves”. Even then, astronomers hypothesized that these gravitational waves are a consequence of an intergalactic collision of our galaxy and a dwarf galaxy-satellite, which could pass on the edge of the milky Way. Scientists from the University of Rochester think they found a suitable candidate for this role. Experts even calculated its approximate mass and current location.
Found in the data of the space telescope Gaia European space Agency Antila 2 was a very unusual dwarf galaxy. It revolves around the milky Way at a distance of 420 000 light-years. Has a very small size – about 7-8 thousand light years, and record low “density sostoyatelnye”. To detect this “galaxy Ghost” was not easy. And not just for its dullness but also because she is hiding behind the bright light of the star jumper of the milky Way.
Using Gaia data, astronomers were able to calculate its trajectory and found that it several hundred million years ago (in the cosmic sense recently) could touch the edge of our galaxy that spawned the wave ripples on its surface. Further calculations showed that the size, speed and location Antlia 2 match the predictions that indicate where in the moment would have to be the originator of a cosmic collision.
The team has also modeled the conditions and the influences that it could have on the milky Way. As it turned out, these models showed similar effects of perturbations of matter currently observed in our galaxy.
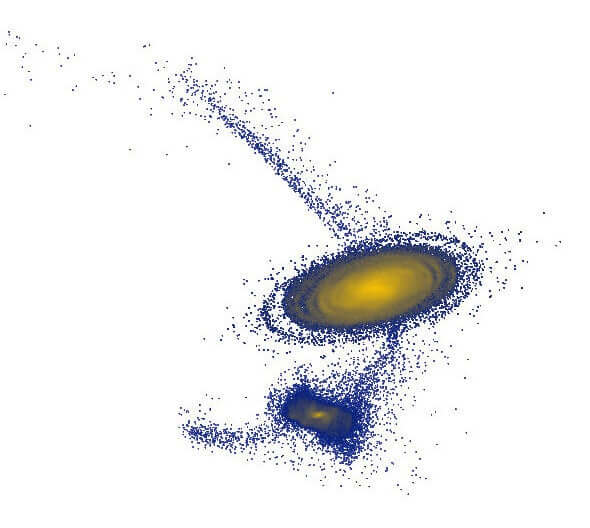
Simulation showing the movement of the galaxy Ghost Antlia 2 (lower concentration) after its collision with the Milky Way (Central cluster)
Finally confirm their assumptions, the researchers decided due to the exclusion of other dwarf galaxies, which could also be culprits of an intergalactic disaster. For example, scientists have found that the dwarf galaxy Sagittarius would not be enough gravitational forces to such effects, and the Large and Small Magellanic clouds are too far away to produce the observed effects.
Of course clash of Antlia 2 with the Milky Way has had a major impact on her. According to the researchers, gravity our galaxy is much more massive, most likely, deprived of Antlia 2 the most part of matter and stars, making it so dim.
To discuss the news in our Telegram chat.