
World DNA is literally a rabbit hole. Each step leads us to new and even frightening discoveries. The more scientists study and hone these molecules of life, the “curiouser and curiouser” become scientific moves. The boundaries between biology and technology blurs, sometimes for the worse. But DNA by itself gives us simple answers about how to treat complex diseases, store information and even looks like a criminal.
Live chip

When scientists dreamed about a new way to look at molecules and processes in cells, in their way stood one obstacle. They wanted to create a device based on DNA, which will act as a single chip to turn on and off. The problem was that the switch needed to activate electricity.
Finally, scientists were able to solve this problem, holding the anthraquinones (the substance is) between the small stretches of DNA. It is a natural compound with the fun adapted for implantation and was able to produce a redox reaction.
During the redox process electrons charged certain molecules, leaving others. The result is an electrical impulse. The stimulation tip electrode anthraquinones coped with this task. Depending on how many electrons they captured, diagrams or conducted a current or not.
Switches, each of which is a thousand times thinner than a hair, are paving the way for microscopic molecular devices. Adapt to this altered genetic code could allow us to study chemical reactions inside cells like never before, with particular emphasis on those associated with the disease.
Injection of DNA cures lameness
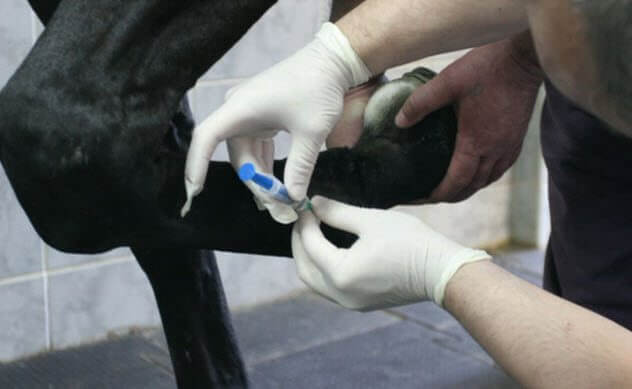
The lame cross-country racers are faced with euthanasia, often with large financial losses for the owner. Often it manifests itself in horses that fall or grow old, but the usual treatment is too long and does not guarantee the quality of life in the future.
Not so long ago this terrible problem was solved by a simple syringe. Researchers took two genes and introduced them at the feet of lame horses. The results were astounding. The injury not only healed, but the horse returned to the racetrack after two months, where he participated in the competition.
Revolutionary genes BMP2 and VEGF164 were injected directly into damaged ligaments and tendons. DNA has encouraged the development of new blood vessels, bones and cartilage that has got great fabric. This treatment is not yet a major, but promises to change a lot as in veterinary hospitals and in hospitals for people. Subjects horses remain in peak condition throughout the year after receiving the treatment, which gives hope that one day this method could help people with the problems of the tendons, torn ligaments, and even spinal cord injuries.
Hook per person
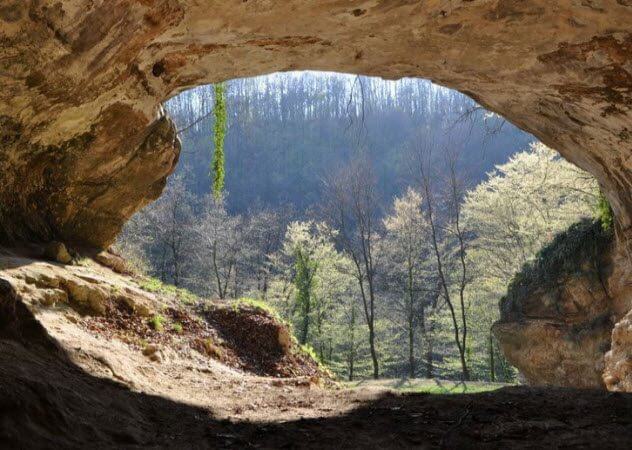

The human lineage remains incomplete, despite decades of research. Anthropologists can investigate only what is available, and the skeletons of the first humans and other hominids not so much. However, new methods allow retrieval of ancient DNA without a body.
In Belgium, Croatia, France, Russia and Spain gathered dirt and sifted on the subject of human DNA. To improve the chances of all 85 samples were taken from archaeological objects by the age of 14 000-550, 000 years. The results of the tests were awash with genes.
In one teaspoon of sand found trillions of DNA fragments. Woolly rhinos, mammoths, cave bears, ancient hyenas — they are all complicated the search for hominids. To remove this genetic noise, researchers have resorted to fishing. They created a kind of hook from modern mitochondrial DNA. Because it belonged to the person she was raised just like the DNA from the mixture of genes.
It is noteworthy that the molecular tool hooked chains of the Neanderthals in places where had never found their bones nor the tools. There was even DNA from an extremely rare representative of the ancestors, Denisovsky person. Fishing technique genes on the hook to answer long-standing questions about which places and artifacts belong to the people, and which Neanderthals or completely unknown hominids.
Genes-tassels

When scientists searched for the DNA complex responsible for the wings of a beautiful butterfly, a surprise awaited them. Instead of the expected network of genes they found only two. Genes WntA and optix behave like a pencil, drawing the contours of the image, and paint that these contours colors.
Previous studies have suggested the involvement of this pair of artists and associated optix with red and orange. But their unique influence were discovered only when scientists began to experiment with these “genes-tassels”.
When WntA disconnected, the order disappeared. The lines faded, the colors blended with each other, the drawings disappeared. Disabling optix led to more interesting results. Butterflies have become gray or black, not only in the wings.
An unexpected twist happened in the case of the usual “big-eyed” butterflies Junonia of coenia. Spots the blue iris was dotted the wings where it wasn’t before. It showed that optix also affects the pigmentation at the physical level.
Both gene appears to have led to major evolutionary changes and abilities, including mimicry as a protection.
Fetal surgery
In an attempt to cure a dangerous blood disease, Chinese scientists have created human embryos in the laboratory. In 2017, the project involved the cloned embryos and tissue taken from a patient suffering from beta-thalassemia.
Like many genetic diseases, beta-thalassemia is caused by failure of the bases in human DNA. The human genetic code consists of four bases — adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine (A, C, G and T). They contain all the guidance on the formation and control of the body.
The abnormal base is called a point mutation. It has always been associated with two thirds of the genetic diseases. To find point mutations for beta-thalassemia, the researchers scanned the three billion “letters” of the genetic code.
It turned out that one of the G was not in place. Method edit reason replaced it with A and cure the disease at the DNA level. In the future, the editing system of reason can give positive results for other hereditary diseases.
The sacrificial skin

Sun lovers will soon be able to enjoy the sun without worrying about skin damage. UV rays from the Sun can destroy DNA and cancer risks associated with tanning, has long been known.
In 2017, scientists have come up with a brilliant idea. Sunscreen made from the DNA of the sperm of salmon, absorbs ultraviolet light almost as a second skin. The longer it irradiates the light of the sun, the better. Those who like to roast for hours will no longer worry about dehydration. Fish film retains moisture.
The use of water and ethanol, can have a wider circulation than just sunscreen. It is a colorless substance can be used as emergency bandaging. Its crystalline nature will also allow doctors to observe the healing, not taking out cover.
DNA can store music
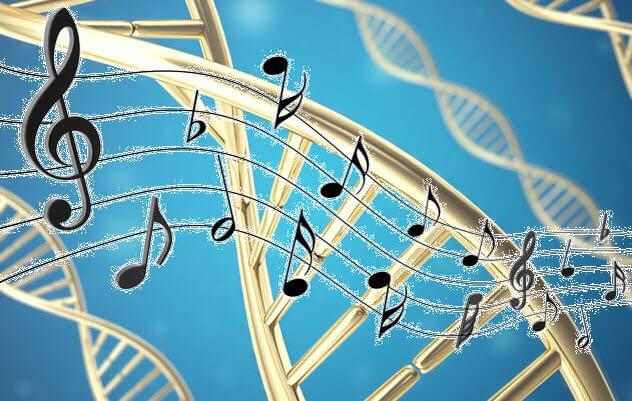

Trying to help the world solve the problem with the storage of information, the researchers turned to DNA. They wanted to prove that no other medium can compare with her savings ability or reliability.
Not long ago, two music — Smoke on the Water (Deep Purple) and Tutu (Miles Davis) — became the DNA files. Their binary code digital language consisting of ones and zeros, was converted into genetic bases (A, C, G and T).
In turn was created synthetic base, located in accordance with the binary sequences of music. Songs took 140 MB on the hard disk. But turning into DNA, they were hardly more than specks of dust. Files were recovered by the treatment process, and no segment has been damaged.
The universal nature of DNA means that thus it is possible to store not only music. Other information that scientists have turned to genetics, included a film, a computer virus, and even whole computer operating system.
The density of such a system will one day save all these Lands in one room. Under certain conditions, genetic files can be stored for thousands of years.
The definition of offenders in the genes

Criminals with genetic information that is stored in databases that have every reason to hate the DNA, left them at the crime scene. The mapping will quickly lead to their conviction or capture. Problem was to blame the perpetrator, not having any prior records. If the crime scene was littered with anonymous genes, and the business was in danger of becoming “blind.”
New forensic technique may make a person a criminal based on his or her genetic remains. The so-called full DNA can tell researchers about the real color of hair, eyes and skin of a person, geographic ancestry, and the finer details such as freckles.
Genes can tell a lot about the physical appearance of a person. To improve his technique and increase the accuracy of determination of the facial traits, the researchers scanned the face and DNA of the volunteers. The software searches for the point of intersection of the genetic dots and shapes of the jaws, cheeks and noses.
Samples that have been identified, made a full able to provide sufficient information to compile digital pictures. On the other hand, it can be used to add detail to the skulls of unidentified victims.
Stealing genes

Water body tihohodka different monstrous vitality, and strange genes. This creature’s genome was sequenced, we learned more about his powers. These microscopic invertebrates can survive in space, at the temperature of freezing and boiling, under incredible pressure, radiation, and decades without food and water.
The reason for all this may be the ability of the animals to steal genes from other life forms. Animals and people walk through the process of horizontal gene transfer, mainly due to viruses. Most species contains 1% alien DNA, while deposits of foreign genes in animals is simply enormous — up to 17.5%.
According to various estimates, 6000 stolen genes belong to the bacteria, fungi, plants and archaea. The animals have a survival mechanism in which they get rid of the water. It destroys their DNA. During rehydration the genome is going back and possibly absorbing other people’s pieces.
Those that are passed to the next generation, makes the animals more tenacious. In particular, bacterial genes are more resilient in extreme conditions than the genes of animals.
DNA can hack into computers
At first glance it may seem that this title is taken from the plot of the movie about spies. But in 2017, scientists at the University of Washington took malware and coded it in synthetic DNA bases.
The leap from biological to digital happened when the computer sequenced chain. When software has changed the combination A, C, G and T, transforming them back into a computer code, the virus was released and gave researchers full remote access to your computer. Although this kind of break-ins are not used currently, they will, give them time.
10 incredible stunts that scientists have done DNA
Ilya Hel