The way models walk on the catwalk is very different from the way we walk in everyday life. However, everyone moves differently and your individual gait can tell you a lot about your body and overall physique. Although it is different for everyone, some illnesses can greatly affect your gait, such as injuries or genetics, and gait disorders include irregular movements such as dragging, waddling or crossing your legs while walking. It is known that walking can reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, but this depends on the speed, which, according to scientific research, can be an indicator of the overall health of the body. Experts note that in recent years, walking has become an increasingly important indicator of vital activity, along with body temperature, pulse rate, breathing and blood pressure.
Your Walk Says a Lot About Your Health and Aging. Image: www.hipkneeortho.com
Contents
- 1 Why Walk?
- 2 What Does Your Gait Say About You?
- 2.1 Pain When Walking
- 2.2 Unsteady Gait
Why Walk?
To improve both physical and mental health, everyone should exercise for at least 30-40 minutes daily. However, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), achieving the recommended amount of exercise per week can be a bit of a challenge. Fortunately, something as simple as walking can help maintain well-being, as it effectively replaces the recommended amount of exercise.
In addition, walking can be done indoors or outdoors, alone or in a group, and the intensity of the load can be easily changed by simply changing the direction and speed of walking. And although most of us believe that we need to walk at least 10,000 a day, many experts disagree with this statement.

Walking is good for your health. Image: www.health.com
Thus, according to therapist Ann Hester, 7,000-8,000 steps a day correspond to the WHO recommendations for physical activity. But the results of previous studies show that health benefits begin to appear after 4,000 steps a day or 10 minutes of walking.
More on the topic: Why is the claim about the benefits of 10,000 steps a day a myth?
Walking can also reduce the risk of dementia. A study published in JAMA Neurology found that walking 9,800 steps may be the “optimal” way to reduce the risk of developing this neurodegenerative disease. At the same time, the results show that just 3,800 steps a day can reduce the risk of dementia by 25%.
And most importantly, walking helps you live longer. A study published in JAMA Internal Medicine found that older women who walk about 4,400 steps a day have a 41% lower risk of premature death. Another study published in JAMA Network Open found that Taking 7,000 steps a day is associated with a 50-70% reduction in the risk of early death.

Want to live longer? Walk as much as possible. Image: images.theconversation.com
Another study, which you can read in the journal Nature, showed that 10 minutes of brisk walking daily can lower your biological age by 16 yearsand add an extra 20 years of life. But what about your gait? And why do scientists believe that it is an excellent indicator of the general condition of the body?
Read even more interesting articles on our channel in Yandex.Zen – there are regularly published articles that are not on the site!
What does your gait say about you?
Despite its apparent simplicity, walking requires the transmission of a huge number of signals between the brain and the muscles of the arms, chest, back, abdomen, pelvis and legs. Yes, what seems relatively simple is actually incredibly complex. And the pace and smoothness of your gait can indicate your health and how quickly you are aging.
That's because with age, muscles lose mass, strength and quality. This process is called sarcopenia and begins around the age of forty. Along with this, the nervous system undergoes “atrophy”, in which brain cells – neurons – die off, as well as their parts: dendrites and axons.
It is estimated that between the ages of 20 and 60, a person loses 0.1% of their neurons each year, after which the loss accelerates. So if you live to be 90, your brain will have lost 150g of tissue compared to its weight at age 50.

With age, brain atrophy occurs, which occurs in the cortex and subcortical parts of the organ. Included in the list of degenerative brain diseases. Image: gbuzspb4.ru
Previous studies have shown that walking speed at age 45 is an important indicator of physical and mental health in later life. True, by the age of 60, walking speed noticeably decreases. This, in turn, means that decreased speed and smoothness of gait may be an early sign of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's disease.
Related: Why walking backwards is good for your health
Recall that Parkinson's disease disrupts the transmission of signals from the brain to the musculoskeletal system, causing a person's gait to become slower, less symmetrical, and unsteady. In the early stages of the disease, these changes may be barely noticeable. As cognitive abilities decline, the length of the step during walking also decreases significantly, and the time it takes to complete a step increases.
Pain when walking
Researchers note that if you feel pain in your gluteal muscles, the back of your legs, and even your calves while walking, which disappears when you stop moving, you may be dealing with peripheral arterial disease(PA) is a common condition in which fatty deposits in the arteries limit blood supply to the leg muscles.
The presence and then absence of pain during movement or rest occurs due to the narrowing of the arteries that supply blood to the lower extremities. This is because when walking, the leg muscles experience an increased need for oxygen, experts explain.
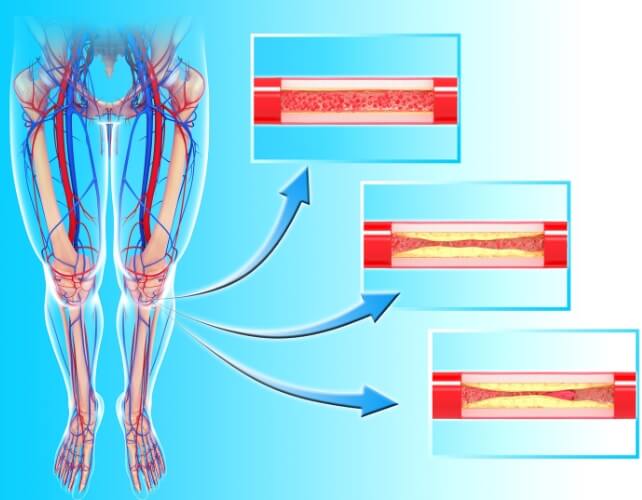
Illustration of narrowing of a peripheral artery due to cholesterol plaques. Image: sciencealert.com
As a result of narrowing of the vessels, arterial blood flowing to the lower extremities cannot satisfy the need for oxygen and the muscles experience a shortage of it. This, in turn, leads to the release of lactic acid, which causes cramps. But as soon as you stop moving, the pain disappears – this happens because at rest, the leg muscles need a minimal amount of oxygen.
Risk factors for developing peripheral arterial disease include smoking, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and diabetes. Having a family history of heart disease is also a risk factor.
Don't Miss: Why Walking Is One of the Best Exercises for Health?
Unsteady Gait
Unsteady gait and balance problems are often associated with excessive alcohol consumption, but can also indicate a vitamin B12 deficiency. While symptoms may take months or even years to appear in adults, they may appear much more quickly in children due to the maturation of the nervous system and the key role of vitamin B12 in protecting it from disorders.
Fortunately, treatment of vitamin B12 deficiency with injections is relatively simple and generally well tolerated. In some cases, adding vitamin B12-rich foods to the diet, such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products, may be enough to eliminate symptoms.

Labyrinthitis is the development of inflammation in the inner ear. The disease can lead to problems with balance and gait. Image: lorlor.ru
Another interesting cause of gait disturbance may be problems with the inner ear, such as labyrinthitis: due to inflammation, a person may experience problems with balance. They usually go away on their own, without treatment. Labyrinthitis leads to a disruption in the movement of fluid in the inner ear, which makes it difficult to interpret nerve signals from the ear to the brain. As a result, the body does not fully interpret visual and positional information.
You will be interested in: Lack of sleep worsens people's gait, their legs begin to “tangle”
It is important to remember that with age, a person's gait inevitably becomes less smooth and easy. However, if you notice that you have begun to stumble, stagger and fall more often, or simply find it more difficult to walk in a short time, you should consult a doctor. Whether you're an experienced athlete or a keen walker, any changes in your gait require attention.
The same goes for doctors, who, according to researchers, should pay close attention to their patients' gait. After all, mobility is a fountain of youth, and paying attention to how we walk is the key to health.