Recently, the very first rocket that went into space turned 80 years old. It is the German V-2 rocket, which in June 1944 first crossed the Karman line – the conventional border between Earth and space, which is located at an altitude of 100 kilometers above sea level. The very first rocket stood 14 meters high, weighed more than 12 tons and flew at a speed of approximately 5.7 thousand kilometers per hour. Much time has passed since then, space rockets have been greatly improved, but the principles of their operation have remained almost unchanged. Now you will learn how rockets work and how they fly into space. As always, everything is extremely brief and in simple words.

Space rockets have been around for almost 100 years, but some people don't understand how they work—it's time to fix that: istockphoto.com
Contents
- 1 How rockets fly into space
- 2 At what speed do rockets fly
- 3 How are space rockets controlled
- 4 What parts do rockets consist of
- 5 Stages of launching a space rocket
How rockets fly into space
Rockets fly into space thanks to two laws of physics.
Newton's first lawstates that any object with mass resists a change in its state of rest or motion. The rocket has engines that create thrust and help it overcome this resistance – due to this, the structure flies upward.

Rocket flights can be explained by Newton’s two laws. Source: lenta.ru
Newton’s third lawsays that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. When a rocket expels gases back, it receives an opposite reaction that pushes it upward toward space.
According to IFL Science, these two laws of physics explain how rockets overcome the force of gravity and are propelled into outer space.< /p>
At what speed do rockets fly
To rise from the ground and fly into space, a rocket needs to gain speed. Scientists' calculations have long shown that to cross the pocket line, the rocket must move at a speed of about 3,500 kilometers per hour. To enter low Earth orbit and stay there, you need to gaina speed of 28,800 kilometers per hour.If you need to leave the Earth's gravitational field, you need to accelerate to 40,000 kilometers per hour.

To reach space, rockets must gain incredible speed. Source: nippon.com
To create thrust to take off and gain speed, rockets use engines. Thrust depends on the speed and mass of gas ejected from the engine nozzles – heat and energy arise when the rocket fuel reacts with the oxidizer. The fuel can be kerosene (Falcon 9 from SpaceX), liquid hydrogen (Space Launch System from NASA) or methane (Starship from SpaceX). Oxidizing agents are usually liquid oxygen, nitrogen tetroxide or ammonium perchlorate.
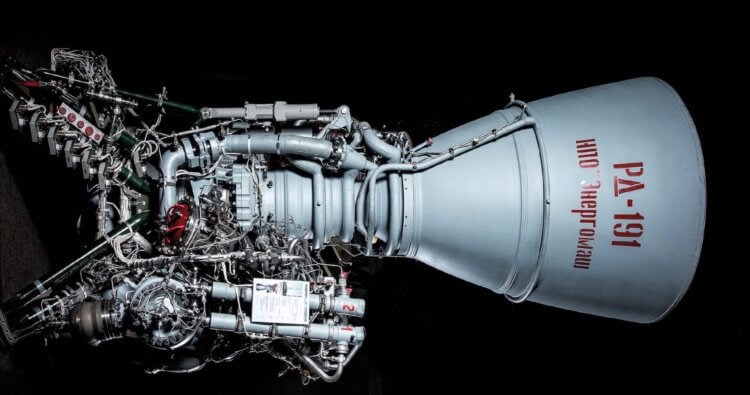
Russian rocket engine RD-191. Source: mentoday.ru
On Earth, the oxidizer is oxygen contained in the air. In space, there is none, so oxidizers are poured directly into rockets.
Read also:The main advantages of the Russian Angara launch vehicles
How space rockets are controlled
During flight, the rocket must be controlled, otherwise it will fly in an arbitrary direction like a deflated balloon. The design has an elongated shape, and the thrust is created on its tail, which is why controlling the rocket resembles holding a pencil on your finger.
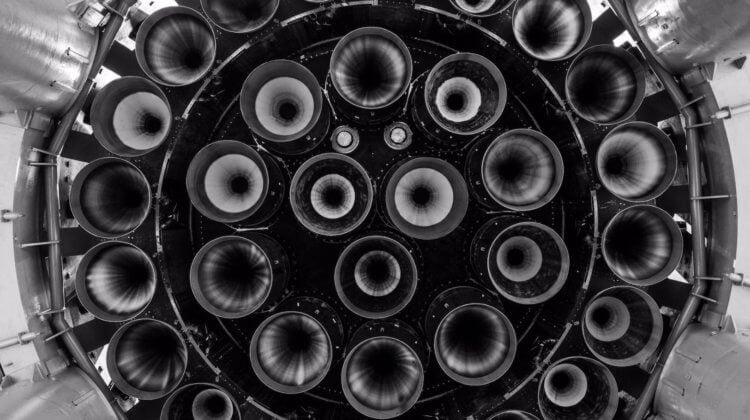
SpaceX Rocket Engines. Source: interestingengineering.com
The rocket uses movable engine nozzles to control it. If they fail, the structure will tumble through the air and eventually crash.
You might be interested in: How does the technology for launching satellites into space without using rockets work?
What parts do rockets consist of?
Modern rockets consist of several parts called stages.
First stage– This is the lowest part of the rocket, which is equipped with the most powerful engines and the maximum amount of fuel. It lifts the rocket from the ground and operates until the fuel tank runs out. After this, the first stage is separated from the structure and either falls into the water or lands on a platform for reuse (only SpaceX has this technology).

Structure of the Russian Soyuz-FG rocket. Source: space4kids.ru
The second stageof the rocket is also equipped with engines and is turned on after the first stage separates. It is needed in order to launch the structure directly into space.
Above the second stage there is a cargo compartment or capsule, inside which there is a payload: satellites, scientific instruments, and so on. Often there is a spacecraft carrying astronauts above the second stage. When the capsule goes into space, it opens and the research vehicles go into outer space. The spacecraft usually flies to the ISS, docks with it, and the researchers find themselves inside the station.
Everyone should know this:Can a piece of a space rocket or satellite fall on a person
< h2>Stages of launching a space rocket
Each launch of a space rocket can be divided into several stages:
- Preparation for launch:the rocket is installed on the launch pad, refueled and the functionality of all systems is checked;
- Countdown: a few minutes before launch, a countdown begins, during which all rocket systems are checked again;
- Switching on the engines: after the countdown, the rocket's first stage engines turn on and it flies upward;
- First stage department:at an altitude of 50 to 150 kilometers, the fuel of the first stage runs out, it separates and either breaks up in the ocean or lands on a landing platform;
- Turning on the second stage: after separation of the first stage, the engines of the second stage are turned on, which further accelerates the structure to enter space;
- Orbit entry: as soon as the structure enters low-Earth orbit, the second stage also separates and burns up in the Earth's atmosphere;
- Mission completion: The cargo bay opens, releasing the payload. If there were people on board, they fly on the ship to the ISS, the Moon, and so on, depending on the mission.
You will find even more interesting materials on scientific topics in our Zen channel. There are already more than 100 thousand people, so subscribe!
The largest, most expensive and powerful rocket of our time is the SpaceX Starship. In the future, it is planned to be used for flights to the Moon and Mars. You may not even realize how huge it is, look for yourself!