In 2005, in one of the coal mines of India, paleontologist Sunil Bajpai found fossilized vertebrae of an animal unknown to science. At first he unearthed only a couple of bones, but over time their number increased to 27 pieces. Further examination revealed that the parts of the spine belonged to an ancient snake, which had a huge body – this was hinted at by the fact that each vertebra was the size of a human fist. Today, researchers know what family this giant belonged to, what kind of life he led and much other interesting information. There is also an assumption that the Indian monster of ancient times was larger than Titanoboa – according to current scientists, the largest snake in the entire history of the Earth.

Judging by the finds of paleontologists, in ancient times there were many huge snakes on Earth
Scientists have discovered a new species of snakes
The vertebrae found in an Indian mine were identical in size and structure, so scientists immediately realized that they belonged to the same animal. After studying the features of the bones, paleontologists came to the conclusion that they had found the remains of a new species of snakes from the extinct family Madtsoiidae. The snake, new to science, lived approximately 47 million years ago and was similar to modern boas and pythons.
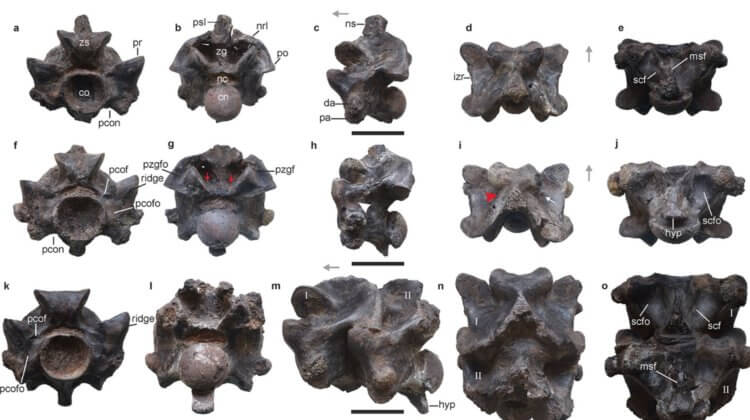
The vertebrae of the ancient snake Vasuki. Image source: nature.com
The ancient snake was named Vasuki inidicus. In Hindu cosmology, Vasuki is a mythical snake of enormous size, which was used by the gods to churn the ocean to obtain the elixir of immortality. According to legend, when Vasuki shook the water, he released a deadly poison, which the Hindu god Shiva agreed to drink in the name of saving the world.
Read also:Why are there so many snakes on Earth?< /p>
What were the ancient snakes
Determining the body length of the ancient snake Vasuki was difficult because its skeleton was incomplete. But with the help of computer modeling and available data on modern snakes, scientists were able to determine the approximate size of the giant. Calculations showed that the length of the Vasuki snake was approximately 15.2 meters.
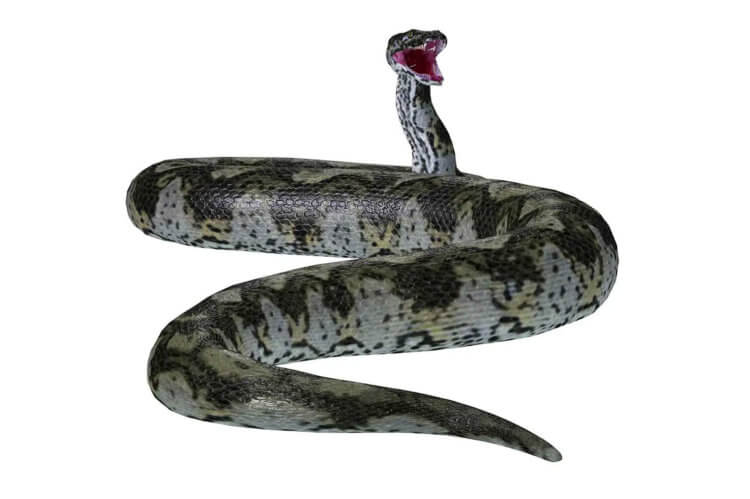

Approximate appearance of a giant snake of the ancient world. Image source: nature.com
Given its large size and similarity to modern boas and pythons, it was a very slow snake. She most likely ambushed victims and squeezed them with her heavy body until they died. The remains were found in a swampy area, which hints that the ancient predator led a semi-aquatic lifestyle. Not far from it, fossils of stingrays, sharks, turtles and crocodiles were found – perhaps some of them were hunted by the giant. And someone from this list could be his natural enemy.
You might be interested:Is the longest snake in the world an anaconda or a reticulated python?
The largest snake in the history of the Earth
Paleontologists believe that the Indian snake Vasuki could be longer than Titanoboa – according to scientists, the longest snake of all. There is very little information about Titanoboa, but researchers believe that it was more than 14.3 meters long. Due to its enormous size, it posed a threat to all living organisms that lived 55 million years ago. My colleague Andrei Zhukov previously spoke about this ancient monster – paleontologists say that Titanoboa could eat crocodiles.
But it is impossible to say with complete certainty that the snake Vasuki was larger than Titanoboa. The fact is that scientists have not yet been able to find a complete skeleton of any of these snakes. And even if they are able to collect a complete set of bones, it is not a fact that the snake found was the largest individual. After all, paleontologists can find the remains of a cub, but adults were clearly larger than him. It cannot be ruled out that some individuals of the snakes Vasuki and Titanoboa grew up to 30 meters – in our world anything is possible.

Comparison of the sizes of the prehistoric snake Titanoboa with and humans. Photo source: my-pet.store
While studying the snake Vasuki, scientists learned something interesting about what the climate was like on Earth 47 million years ago. It is known that all snakes on Earth are ectotherms, that is, cold-blooded animals. Their body temperature directly depends on the temperature of the environment, that is, such large creatures could not live in cold conditions. Based on this, scientists concluded that during the existence of Vasuki snakes in the lands of present-day India, the average air temperature was +28 degrees Celsius. That is, the climate was very warm.
Do you want to stay updated on new scientific discoveries? Subscribe to our Telegram channel!
What caused the extinction of Vasuki snakes is not clear. The most plausible version is that they disappeared due to climate change. Perhaps it is good that they are not there now – they would pose a great threat to us. Snakes are already very dangerous animals because they have poisonous fangs. For example, a black mamba is able to catch up with anyone and kill with its poison with 100% probability.