Dinosaurs went extinct approximately 66 million years ago, and since then the animal world of our planet has changed greatly. After the asteroid hit, in addition to dinosaurs, many other animal species became extinct. Terrestrial ecosystems were devastated, opening the door for tiny mammals to fill the vacated ecological niches. At first they were very primitive creatures, but over the course of evolution they became more and more complex and larger. Finding their remains is very difficult, and each such discovery becomes sensational. For example, bones of a small and cute-looking creature, from which modern cows, pigs and deer originated, were recently discovered in the US state of Colorado.

Scientists have talked about the animal that is the “father” of all modern ungulates
< h2>Who lived after the extinction of the dinosaurs
According to a new article in the scientific journal Mammalian Evolution, the ancestor of modern ungulates is a small animal of the species Militocodon lydae. The order of ungulates includes not only cows, pigs and deer, but also rhinoceroses, giraffes and many other animals.
The ancestor of modern ungulates lived about 65 million years ago, almost immediately after the extinction of the dinosaurs. It was comparable in size to a rat and weighed about 455 grams. The ancient creature was tiny, but he managed to evolve and become the ancestor of huge animals thanks to the fact that he no longer saw the threat from bloodthirsty dinosaurs. Conditions for development after the asteroid impact turned out to be ideal.

The ancient animal Militocodon lydae as imagined by an artist. Image source: sciencealert.com
The peculiarities of the ancient animal became known after the discovery of fragments of its skull at the Corral Bluffs excavation site, which is located in the state of Colorado. There, scientists have long found deposits more than 60 million years old, which correspond to the Paleocene era.
Read also:The strangest animals whose existence is hard to believe
Where did pigs come from?It was possible to determine that Militocodon lydae was the ancestor of modern cows and pigs thanks to careful cleaning of the skull and complex 3D scanning. Analysis of the teeth and their comparison with the jaws of other animals showed that the animal was not a rodent. Its teeth were adapted exclusively for crushing food, so it is highly likely that it really is the ancestor of cows and deer with similar jaws.
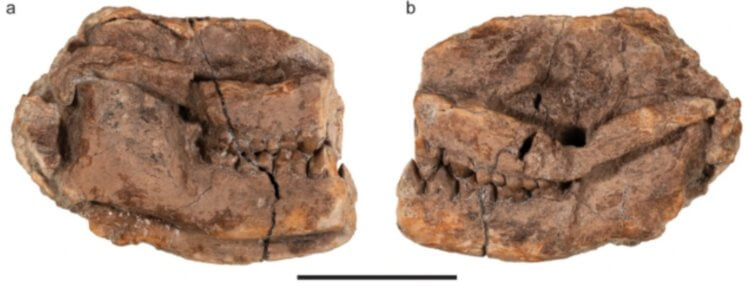
The skull of the ancient mammal Militocodon lydae. Image source: sciencealert.com
This is not the first remains of a tiny creature found by scientists. Over the past eight years they have found several more bones, but they are all very small. So many features of Militocodon lydae still remain a mystery to scientists. They intend to continue to search and study the remains, because this is very important for understanding what the world was like after the extinction of the dinosaurs.
You will be interested in:The most amazing dinosaurs that lived on territory of Russia millions of years ago
What were the ancient animals
The remains of animals from the ancient world such as Militocodon lydae help to understand the evolution of periptychids (Periptychidae). This is the name of a family of extinct mammals that began to actively evolve in a safe world without dinosaurs. Their fossilized remains are found in Paleocene deposits, which, in addition to Colorado, are found in the territories of Canada, China and even Uzbekistan.
The discovery and detailed descriptions and comparisons of part of the skull of Militocodon lydae represent an important step towards unraveling the complex evolutionary history of periptychid mammals, said paleontologist Lucas Weaver.

Among the representatives of the periptychids family there were also large animals. Image source: popsci.com
Representatives of the periptychid family could be both small and large. Whatever the physique of these creatures, their limbs were short and strong. The teeth of ancient creatures were large, designed for chewing plant foods. Therefore, most of them were herbivores. There are hints of the existence of omnivorous periptychids, but scientists currently have no convincing evidence for this. They could live in different places, ranging from forests to open spaces.
Be sure to subscribe to our Zen and Telegram channels. This way you won't miss any important scientific discovery!
The study of the ancestors of modern animals is the main task of paleontologists. In 2022, they managed to find the remains of one of the very first true predators in the world, and this was a very important discovery from a scientific point of view. Scientists are also able to look even further into the past and talk about the characteristics of the very first ancestor of all life on Earth. This microscopic organism is known as LUCA (Last Universal Common Ancestor) and it was able to survive even in the most extreme conditions.