After 50 years, many people, many people, face the problem of bone fragility, and the spine often suffers. As a result, various diseases of the musculoskeletal system and even fractures occur. For example, in Europe, more people die from fragility and brittleness of bones than from cancer. Moreover, problems associated with low bone quality are usually discovered only after a person has a fracture, that is, when the disease is advanced. At the stage when the bones are just beginning to lose density, there are simply no symptoms. Of course, there are now various methods that allow you to assess the quality of bones. But how do you know if a person needs to be tested? In a recent study, scientists found out how you can independently determine the risk of having this health problem.
Scientists have told how to determine if you have a high risk of bone fracture
Fat in the body affects quality of bones
In their recent study, researchers at the National Kapodistrian University of Athens recruited 14 men and 101 women with an average age of about 62 years. As mentioned above, most often problems with bone strength occur at this age. The objective of this work was to discover the relationship between excess fat in the human body and the quality of its bones.
As it turned out, such a connection does exist – people with excess body fat, regardless of body mass index, have low bone quality in the spine. Moreover, the more visceral fat a person has, that is, fat located in the abdominal cavity around the internal organs, the lower the quality of the spongy bone of the spine, which is also called trabecular bone.
True, the study does not say anything about cause and effect, that is, whether visceral fat causes deterioration in bone quality or whether visceral fat and bone fragility arise from metabolic disorders. However, it has long been known that visceral fat causes various fatal diseases.
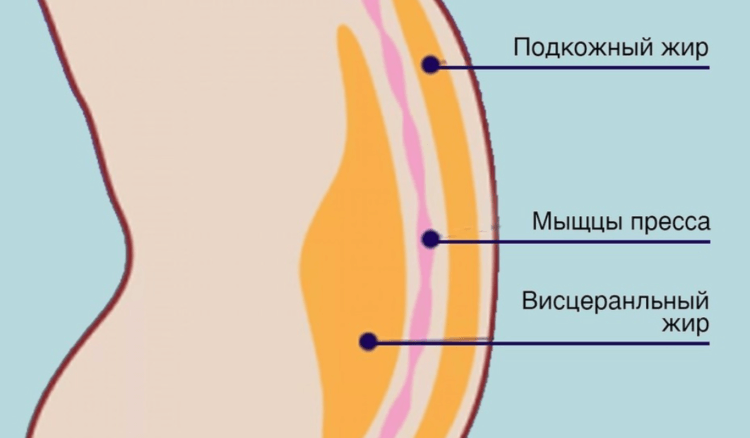
Visceral fat is formed inside the abdominal cavity. Image source: rg62.info
According to scientists themselves, perhaps the reason for poor bone quality is due to the fact that visceral fat produces molecules called adipocytokines. These molecules provoke low-grade inflammation. The inflammatory process most likely has a negative effect on the bones. But for now this is only an assumption that requires confirmation.
How to detect the risk of a spinal fracture
Since visceral fat is located in the abdominal cavity, its presence in the body is quite difficult to detect. As we discussed in the article about the relationship between smoking and body fat, if you have visceral fat, a person's stomach can remain flat or almost flat. Accordingly, it is impossible to determine the risk of fracture based on visceral fat in practice.
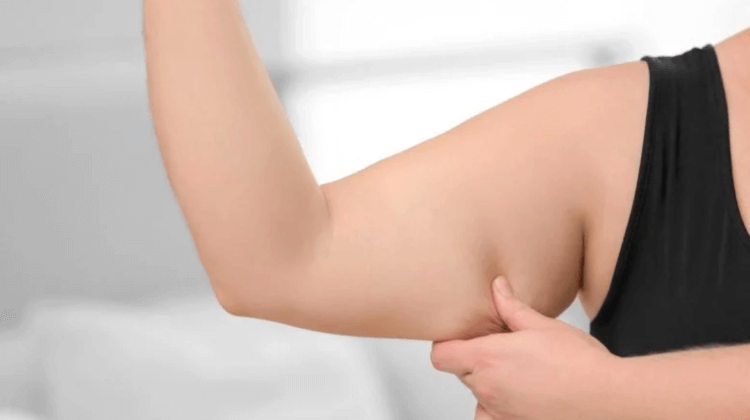
You can assess the risk of fractures by looking at the fat on your arms. Photo source: scitechdaily.com
Therefore, scientists continued the study and decided to find out whether there is a connection between subcutaneous fat and poor bone quality. As SciTechDaily reports, scientists have found that people with excess arm fat are more likely to have poor bone quality and a brittle spine. By the way, this is the first study to show that fat mass in the arms is negatively associated with the strength of bones and vertebrae.
Given the results of the study, it is not difficult to check the risk of a fracture – you need to tense the muscles of your arm and feel it with two fingers of your other hand, as shown in the photo. If, when pressing, the hand is soft and folds form, then there is a large amount of fat present. In this case, it makes sense to conduct additional diagnostics. Bone quality can be determined using techniques such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) or trabecular bone scoring (TBS).

To get rid of visceral fat and prevent bone quality from deteriorating, you need to exercise
Now scientists want to conduct additional research and involve more people in it. They also plan to develop an exercise program that targets visceral fat as well as arm fat. Perhaps this will improve bone quality. True, it’s unlikely that you’ll be able to find universal exercises.
Don’t forget to subscribe to our Zen and Telegram channels so you don’t miss the most interesting and incredible scientific discoveries!
As we said earlier, it is impossible to get rid of fat in only one area of the body through physical activity. Subcutaneous fat is consumed by the body as needed, and it does not matter what muscles a person tenses.