In 2021, there was one more research vehicle on the planet Mars – the NASA aerospace agency delivered the Perseverance rover there. This robot was given the enormous task of collecting samples of Martian soil. Scientists believe that at the bottom of the Jezero crater billions of years ago there was liquid water in which Martian organisms lived. Researchers want to bring soil samples to Earth to study them in the laboratory. If they are lucky, they will be able to prove that we are not alone in the Universe, and at least there was once life on the Red Planet, and maybe it still exists. Everything was going great, but recently it turned out that NASA overestimated its strength. The agency cannot deliver Martian soil to Earth on its own and is now asking for help from private companies.
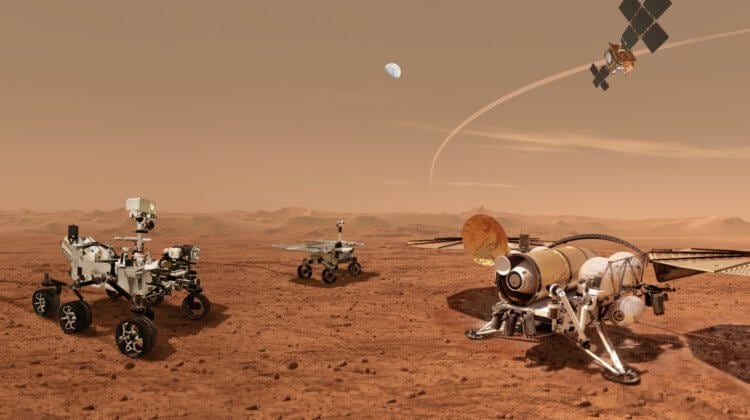

NASA has admitted that it will not be able to deliver Mars samples to Earth under its previous plan. Source: mars.nasa.gov
Contents
- 1 Collection of Martian soil samples
- 2 Delivery of Martian soil soil to Earth
- 3 How much does it cost to explore Mars
- 4 The future of the Perseverance mission
- 5 Sending people to Mars
Collection samples of Martian soil
The cost of the Perseverance mission is estimated at $2.4 billion. But these are only the expenses for the first three years, during which the rover of the same name managed to travel around the Jezero crater along with its satellite, the Ingenuity helicopter. Despite the problems encountered, the rover successfully collected 24 samples of Martian soil. In fact, capsules with valuable material are already ready to be sent to Earth, but NASA did not expect that this would be such a difficult task.
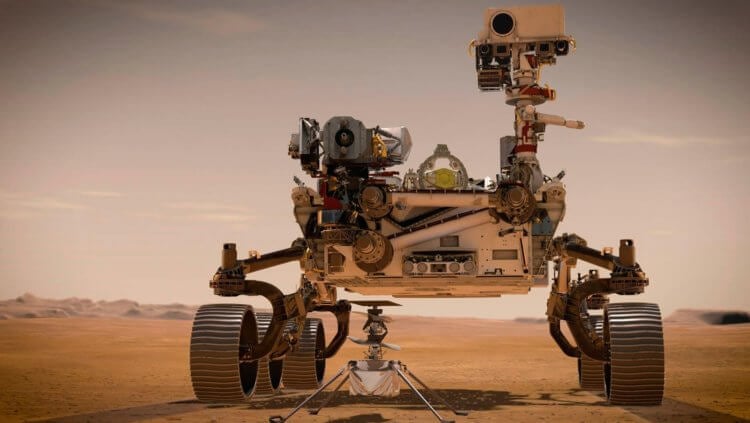
Perseverance rover and Ingenuity helicopter. Source: nasa.gov
Important news:The Mars helicopter Ingenuity has broken down – its mission is officially completed
Delivering Martian soil to Earth
According to the original plan, by about 2030 two rockets were supposed to go to Mars at once. NASA experts wanted to load a landing module on board the first one, and place an orbital vehicle inside the second one.
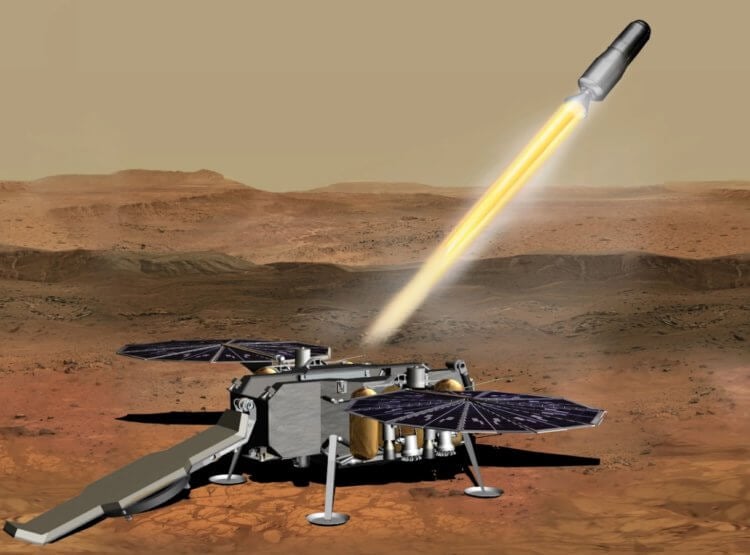

In NASA's view, sending soil into Mars orbit looks like this. Source: sciencealert.com
The largest lander ever created was planned to land on the surface of Mars. It was assumed that he would take capsules with Martian soil and place them inside a small rocket. At the next stage of the mission, this rocket was supposed to fly into the orbit of Mars and transfer soil samples to the orbiter, which would deliver the capsules to Earth.
Read also: Perhaps the Perseverance rover has been around for a long time found traces of life on Mars
How much does it cost to explore Mars
The plan seemed ideal, and NASA representatives wanted to keep it to $4 billion. But then it became clear that engineers would only be able to develop rockets and vehicles for delivering Martian soil to Earth by the 2040s, and this would require up to 11 billion dollars. According to NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, this is too long and expensive, because in two decades, astronauts should already land on Mars in person, and not wait for a box of soil samples.
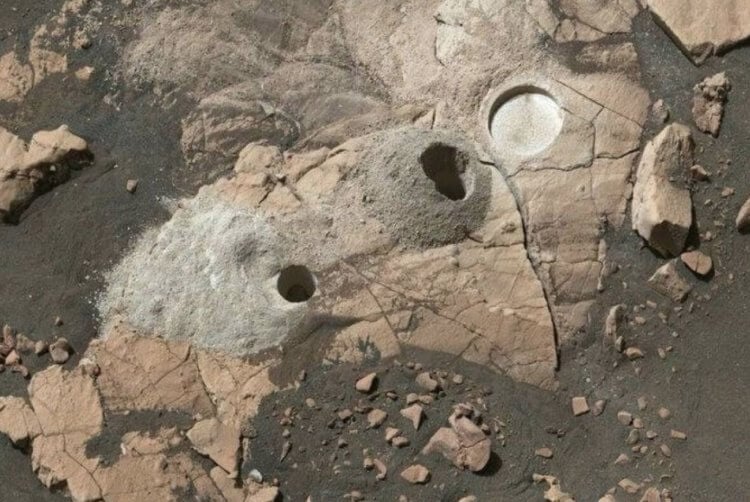

Holes made by the Perseverance rover to extract soil. Source: nasa.gov
The future of the Perseverance mission
NASA representatives do not want to put up with the disadvantages of the old plan to send soil from Mars to Earth. Now they need a new strategy, and the agency has asked private aerospace companies like Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, Boeing and SpaceX for help. They have until May 17, 2024, to develop and submit to NASA a new plan that will be faster and cheaper than the old one. If management likes any of the options, the authors will become official contractors of the agency.

Perhaps Elon Musk will once again come to the rescue. Source: ccn.com
So now we need to wait until mid-May for the situation around the Martian soil samples to somehow be resolved. If we know something interesting, we will definitely tell you about it, so subscribe to our Zen channel. There you can leave comments.
You will be surprised:You have no idea how big the SpaceX StarShip rocket is
Sending people to Mars
In the 20th century, humanity took its first steps beyond the Earth. In the 21st century, we will see how people fully explore the Moon and Mars: they build bases there and even lay railways between them.

An ideal lunar colony would look like this. Source: itcrumbs.ru
Recently, American entrepreneur Elon Musk said that he wants to send a million people to Mars. To do this, the head of SpaceX plans to build hundreds of new generation Starship spaceships (today the company is testing only prototypes) and develop a system for refueling them in space. He immediately warned that the first people on Mars were unlikely to return back; they would only have a one-way ticket. And even earlier he said that during the first flights people may well die.
Are you already in our Telegram chat? We arrange interesting quizzes there every day, join us!
The planet Mars has been of interest to people for a long time. Astronomers have been studying it for hundreds of years, and during this time they have learned a lot of new things about it. You can read more about this in our article “The 7 most important discoveries that scientists made while studying Mars.”