Treatment of cancer is the scourge of modern medicine. The fact is that in the early stages, most neoplasms respond well to treatment, but in the later stages the prognosis is often disappointing. And since cancer is a group of more than 100 diseases that develop over time and are associated with uncontrolled cell division, there is simply no universal treatment method. Fortunately, scientists are constantly working on new methods of treating cancer, and some of them show impressive results. One of these is CAR-T therapy, used in the treatment of hematological malignancies and solid tumors, including brain tumors. In this article we look at what CAR-T therapy is and why scientists pay so much attention to it.
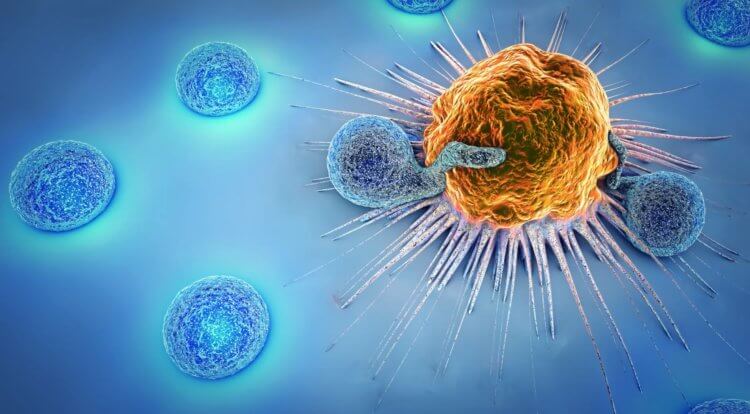
CAR-T therapy has proven effective for more than just leukemia.
Image: www.beckman. com
Contents
- 1 T cells are peacekeepers of the immune system
- 2 What is CAR-T therapy?
- 3 CAR-T therapy for the treatment of glioblastoma
- 3.1 Glioma and glioblastoma
T cells are immune peacekeepers systems
CAR T-cell therapy is a type of immunotherapy also called adaptive cell transfer (ATC), an immunotherapy agent designed to enhance the natural ability of T cells to kill cancer cells. Recall thatT cells(regulatory T cells, suppressor T cells, Tregs) control the strength and duration of the immune response, for which they are often calledpeacekeepers of the immune system. But what exactly do T cells do in the body?
White blood cells called lymphocytes play an important role in fighting infections and diseases, including cancer, and in the human body there are different types of lymphocytes and T cells are one of them.
Modified T cells from leukemia and lymphoma patients help patients get better. Image: www.mypathologyreport.ca
Read also: Russian scientists are close to creating a vaccine against cancer. What is known about her?
As T cells move throughout the body, they search for and destroy defective cells. Their production begins when we come into contact with a new infection or disease. Once the disease is defeated, the body leaves some T cells in reserve so that if we encounter a previous infection again, the body can recognize it and immediately attack the intruder. And although T cells are good at fighting infection, they can have difficulty distinguishing a cancer cell from a normal one.
What is CAR T therapy?
Since cancer cells «deceive» immune system, scientists are trying to find ways to make T cells recognize them. One possible way to do this could be CAR-T therapy – an extremely complex treatment in which a specialist selects a patient's T cells and makes small changes to them in a laboratory setting. The process of collecting samples of a patient's T cells is calledapheresis.
Basic «magic» CAR-T therapy occurs in a laboratory. By making changes to a patient's T cells, scientists train them to recognize a specific protein and target cancer cells. The modified T cells then grow and multiply in the laboratory until they have the required number. Once this happens, the genetically modified T cells are injected into the patient's blood via an IV. The goal of the procedure is to getCAR T cells to recognize and attack cancer cells.
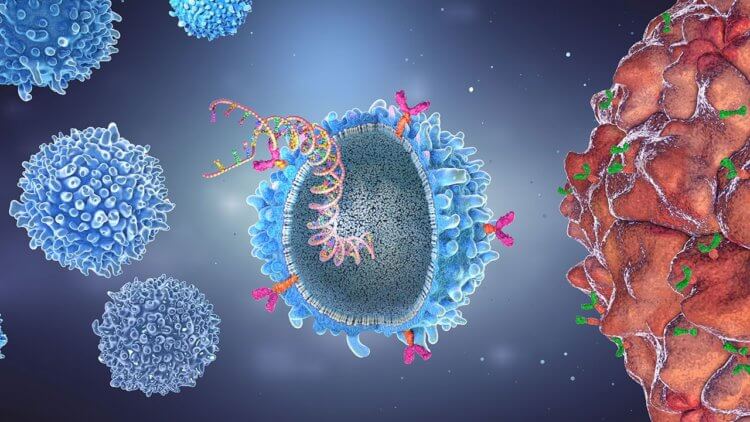
CAR-T therapy is a new word in the treatment of oncology. Image: www.beckman.com
The changes scientists make to T cells in the laboratory mean «improved» the cells can remain in the patient's body for a long period of time, recognizing and attacking specific cancer cells. Researchers are still figuring out how long they can stay in the body. Today, CAR-T therapy is used in children with leukemia and some adults with lymphoma.
Do you want to always be aware of the latest news from the world of science and high technology? Subscribe to our channel on Telegram – so you definitely won’t miss anything interesting!
CAR-T therapy for the treatment of glioblastoma
Although CAR-T therapy (i.e. chimeric antigen receptor therapy) is an established treatment for hematological malignancies, it is also used for solid tumors, including brain tumors.
Thus, during the first phase of clinical trials conducted at City of Hope, CAR-T therapy was studied for recurrent glioblastoma and glioma – malignant brain tumors. The study involved 65 patients, and the researchers tested different delivery methods and technologies for producing genetically modified T cells. The results found that the treatment was safe and well toleratedwith manageable side effects.
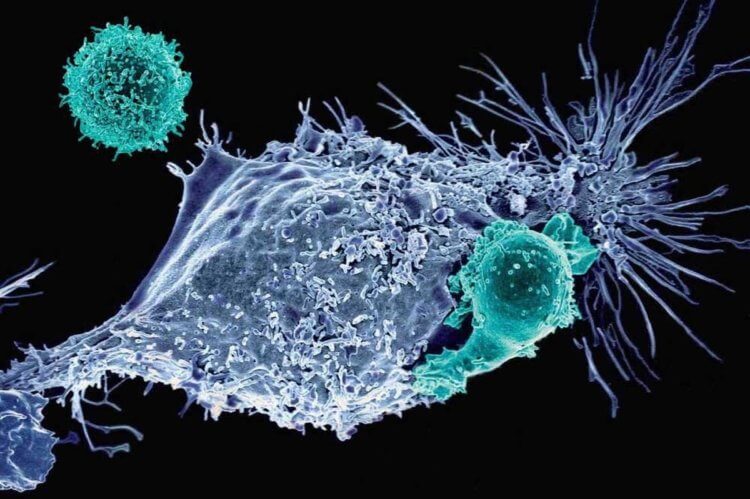
CAR-T therapy has shown promising results in the treatment of brain tumors
Don't miss : Zika virus has proven to be an effective treatment against cancer
Importantly, half of the patients experienced stable disease or improvement, including complete tumor resolution in several cases. Patient survival rates were also encouraging, with a median overall survival of 7.7 months. The full text of the scientific work can be found here. The study results suggest that CAR-T therapy targeting a specific receptor (IL13Ra2) is a promising treatment option for patients with recurrent glioma.
We have achieved exciting results in the field of cell therapy that can target glioblastoma and other glioma brain malignancies. “We think we are getting closer to the goal of developing meaningful therapy for these patients,” Dr. Brown, one of the study’s lead authors, told Targeted OncologyTM.
Glioma and glioblastoma
Malignant brain tumors such as glioma and glioblastoma are essentially a death sentence. This is because tumor cells grow into surrounding tissues and destroy them extremely quickly. Thus, the average lifespan of patients with glioblastoma (the most malignant of gliomas) is on average a little more than a year. Note that experts identify many reasons that make it difficult to treat glioblastoma, and one of the main problems is that These tumors are very invasive and cannot be completely removed surgically.
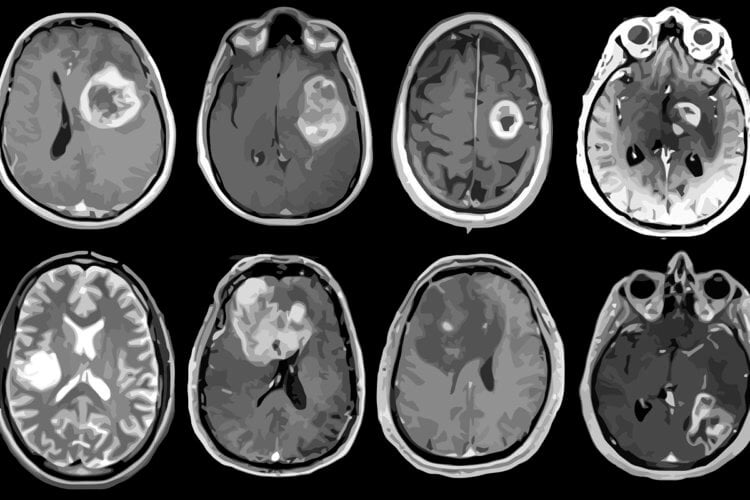
Glioblastoma is a tumor belonging to the group of tumors – gliomas. Glioma (glial tumor) is a tumor that can develop in the brain or spinal cord. These tumors develop from glial cells – neuroglia, which were originally considered nervous connective tissues.
Image: medicine.wustl.edu
You may be interested: a 13-year-old boy was cured of fatal brain cancer for the first time in history< /p>
In addition, gliomas and glioblastomas are heterogeneous, and a number of drugs that target specific oncogenic pathways in other cancers do not work because glioblastoma changes and becomes more aggressive over time. To complicate matters, drugs developed to treat other types of cancer do not penetrate beyond the tumor. Finally, immunotherapy is not very effective against brain tumors.
In short, the treatment and management of patients with malignant brain tumors is an extremely difficult task, and much progress has not been achieved in recent years. But because glioblastomas remain localized in the brain and rarely metastasize to other organs, local CAR-T therapy may be effective.
Gliomas are primary tumors that form in the brain parenchyma. Image: static.tnn.in
You may be interested in: A new look at cancer: what is the parasitic theory of cancer?
Experts also note that many types of cancer of the central nervous system (CNS) ) are refractory to many treatments but respond well to T-cell therapy. Of course, this is not the time for sensational conclusions and further research is needed, but the results published in Nature are promising and give hope to patients with malignant brain tumors.