Official site of the German centre for aviation and Astronautics (DLR) reports that the drilling rig HP3 “Mole” of the Mars lander, NASA InSight, launched from Earth in may of last year and successfully landing on the red planet in November, for the first time, boring the soil of Mars, deep under the surface at 18-50 cm. During the first four hours the engineers created a cent the drill struck a total of 4 thousands of hits, which allowed to reach a level of depth.
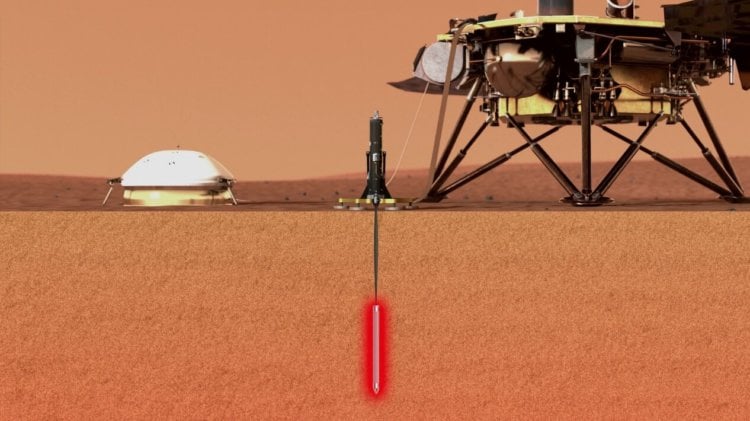
According to the source, in the course of the dive drill has been faced with stone.
“Deeper drilling установкаНР3, apparently, stumbled on a rock, leaned about 15 degrees and either moved it, or has passed”, — says project Manager HP3 Tilman Veneer.
“Going down a little deeper, the unit has reached another stone. But by this time ended his 4-hour shift work. As shown by tests on the Ground, the plant is able to move small stones to the side, which can significantly reduce the time to complete the tasks”, — adds the expert.
As noted by DLR, after the end of the cooling period, the researchers intend to begin the second phase of the drilling rig HP3, which will also last four hours. Scientists plan in the coming weeks to deepen HP3 to the surface of the Martian soil at three to five meters, allowing to measure the flow of heat from the interior of Mars.
The main task of the lander InSight is to study the geological structure of Mars, which he equipped with a seismometer and other instruments. Drilling rig module is completely Autonomous. It is powered by electricity, which was located on the surface of the red planet module, receives from the sunlight.
Because the drilling process creates friction, which heats up as the drill itself and the environment within the hole, it may interfere in the calculations of the thermal conductivity of the soil. So after each four-hour shifts borax need time to cool for approximately three Martian days (sols).
The heat inside of the hole is measured with a special sensor integrated into the drilling rig. In the outer shell of the shock mechanism is a special metal plate. Hot environment and borax is heated and the flap. Reading this disc allows you to determine the level of heat flux of the interior of Mars. In addition, the lander InSight, there is a radiometer, which the apparatus carries out measurements of temperature changes on the surface of the red planet. Vary it can range from a few degrees above zero to -100 degrees Celsius.
Data from temperature sensors as well as sensor for measurement of thermal conductivity, then sent to the control center of the mission at the DLR, and then transferred for analysis and study by the specialists of the Institute of planetary research DLR.
To discuss the progress of the mission in our Telegram chat.