
One of the biggest surprises for mankind was not the fact that space is expanding, and what expanding faster and faster. The farther the galaxy is from us the faster they are removed from us. At some point, as you might guess, these galaxies will move away from us faster than the speed of light, which means you will not only never reach, but do not even see. Why? How many galaxies disappeared from our sight? Depending on what is meant by “disappeared”, the answer can be: all or nothing. Let’s deal.
Our whole cosmic story theoretically well understood but only in a qualitative sense. That is due to observational confirmation, and expose various stages of the development of the Universe in the past, which was to take place, such as the formation of the first stars and galaxies. We think we understand space, and not unreasonably. The big Bang sets a fundamental limit to how far we can look in any direction.
In General, we see the galaxy for the following reasons:
- they form a star
- which create a light,
- who travels around the Universe,
- which expands
- until it reaches our eyes.
Everything seems to be simple enough. Yes? So when we look at the Universe, we expect to see galaxies everywhere and anywhere. Just don’t see it.
The first reason is quite simple: the Universe had a limited amount of time to do it all. The big Bang gave birth to the Universe about 13.8 billion years ago, and the first stars formed after tens or hundreds of millions of years. Right now the very first light comes to the eyes and lenses of our sophisticated equipment. Gradually comes the light from more distant galaxies.
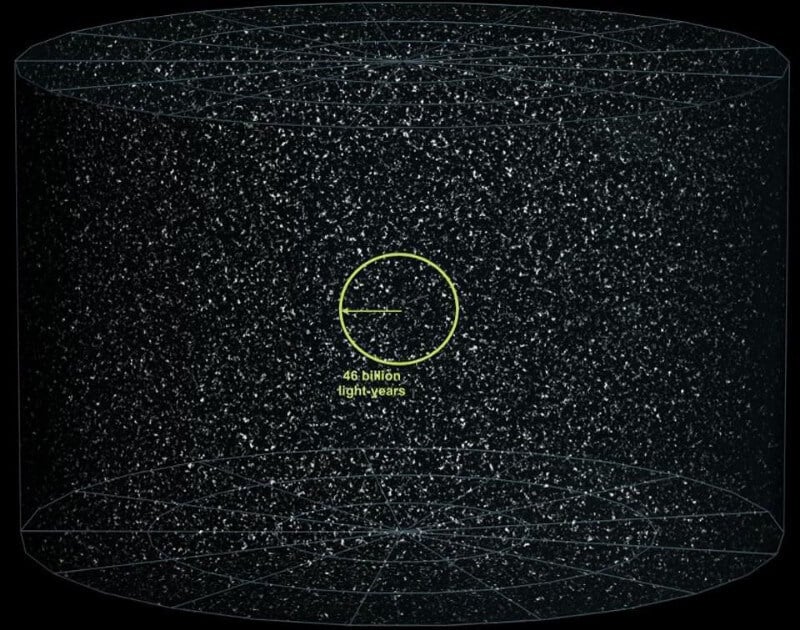
Not all galaxies are visible. Our universe has been expanding for what it was: a mixture of radiation, neutrinos, normal matter, dark matter and dark energy. Based on the history of the Universe, the light can arrive from a distance of 46 billion light years.
But this does not mean that the object that is now 46 billion light years, it will emit something that we will be able to see. It just means that if the object were emitting light 13.8 billion years ago, we get this light now, after 13.8 billion years. And this means that the object that emitted it then, today would be 46 billion light years from us. This is the limit of what we can see in the observable Universe.
It is easy to calculate that we will be able to see only no more than 2 trillions of galaxies. This is a huge number, and gradually they will open up to us. All the galaxies that we have ever seen, as long as they have stars, not going anywhere, plus opens a new. Even the fact that the expansion of the Universe is accelerating, doesn’t change that. As soon as the light arrives from a distant object until the object is emitting photons, the expansion of the Universe will not stop their arrival. In this respect, out of sight, disappeared no one galaxy.
But the expansion of the Universe, especially accelerating, will influence the following two things:
- In the future there will be a limit to how far we will be able to observe distant objects.
- The limit still exists today, and it changes over time, as to how far galaxy could be from us and send us a new light.
Today we can look at best 46 billion light years. This is the current limit of visibility. We can calculate the future and limit visibility and to find that it is 33% more current: 61 billion light years. One day we will be able to observe of the order of 4.7 trillion galaxies, and after enough time will arrive and light sverhdorogih galaxies.
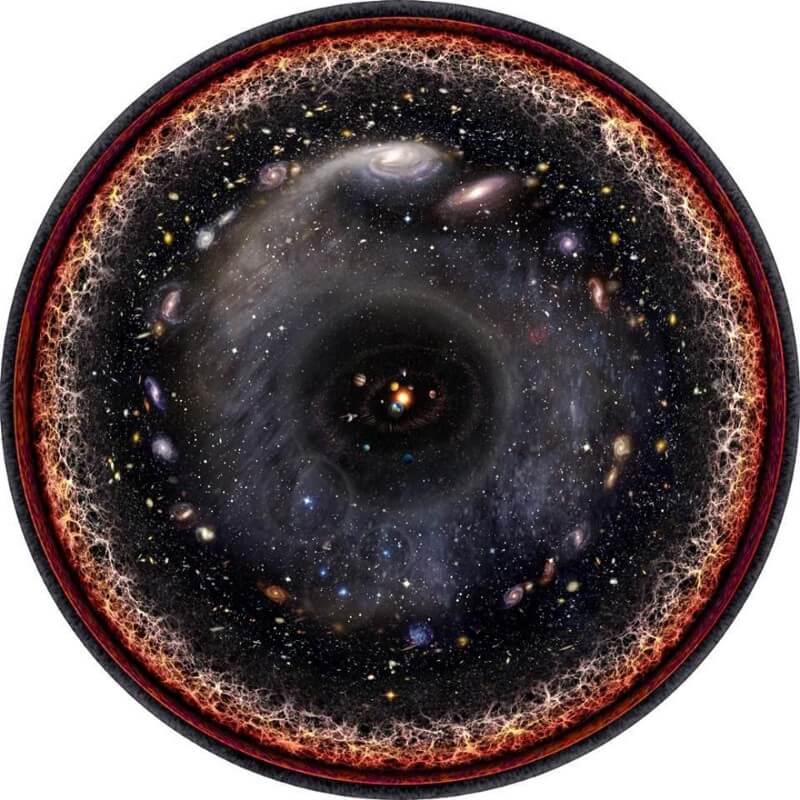

But it’s mostly the light that from our point of view, was emitted billions of years ago. When we look at the distant Universe, we not only look back in time, but we see galaxy which are long gone. Therefore, the light that these galaxies emit today, after 13.8 billion years after the Big Bang, never we will not come. The fact that the universe is expanding and its expansion is accelerating. Distant galaxies are not only receding from us in the process of stretching the fabric of space, but also do it faster and faster. Now galaxy beyond 15-16 billion light-years away from us faster than the speed of light.
That is, even if we went on a space ship that travels near the speed of light, we never would have got to these galaxies. The light that we radiate today, I will not come, as their light to us. And then:
- 96.7% of galaxies that we can observe today, is gone forever.
- 98.6% of the galaxies that we will ever see are already gone forever.
- Approximately 66 billion galaxies is still achievable for us today.
In other words, in the future we will have a total of 4.7 trillion galaxies for review. And 4,634 trillion of them forever unattainable, even if you move them at the speed of light.
This is a problem that will only get worse. Now, if we assume that in each of these 66 billion galaxies just as many stars as in the milky Way is 400 billion, it means that about 60 000 stars disappear from our sight every second. 300 000 stars, disappeared while you were reading this sentence. And another 200 000 until reading this. We will still be able to see them the old world, but any new set up their light will never reach us.
Of course, we will be the Universe for research. We still see the most distant galaxies, even those who will never achieve by just looking at their old light. But every time less and less of the Universe remains at arm’s length. More than 98% of all galaxies, which we visually explore, never shelter our brother. Every moment of inaction disappears a chance to contact.
How many galaxies we will never see?
Ilya Hel