
While the rest of the world is watching and waiting for new information about Starman (dummy SpaceX, dressed in its new space suit and sitting in the driver’s seat of the Tesla elektriraudtee, heading in the direction of Mars), space Agency NASA has published the most far in the history of human space photo taken by the spacecraft “New horizons”. At the time of performing photography (5 December 2017) the unit was 6.12 billion kilometers from Earth.
In addition to the record range from photos “New horizons” there are other stunning features. The station managed to capture a few Kuiper belt objects located at a distance of 55 astronomical units from Earth, beyond the orbit of Neptune. The belt consists of small celestial bodies and clusters of various substances, such as ice, ammonia and methane.
Recall that one astronomical unit is equal to 149,6 million kilometers, that is, the distance from the Earth to the Sun. Thus, objects that managed to capture the New Horizons are from us at a distance of over eight billion kilometers. In particular, the station, moving to our main goal – object in the Kuiper belt 2014 MU69 – managed to obtain images of several dwarf planets in 2012 2012 HE85 HZ84 and made in conventional colours.
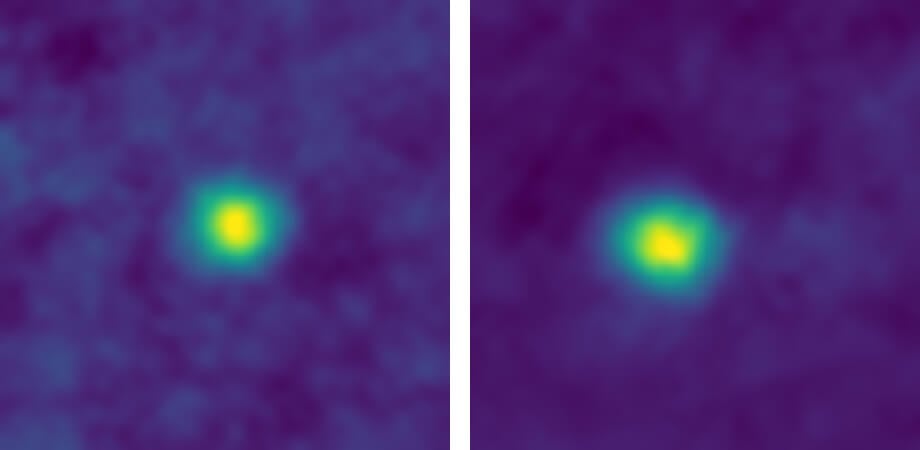
The Kuiper belt objects 2012 HZ84 (left) and 2012 HE85 (right)
On the same day, but two hours previously, the unit has made another photo. This time the object of the picture was made by a more distant goal – a star cluster the wishing Well cluster (NGC 3532).
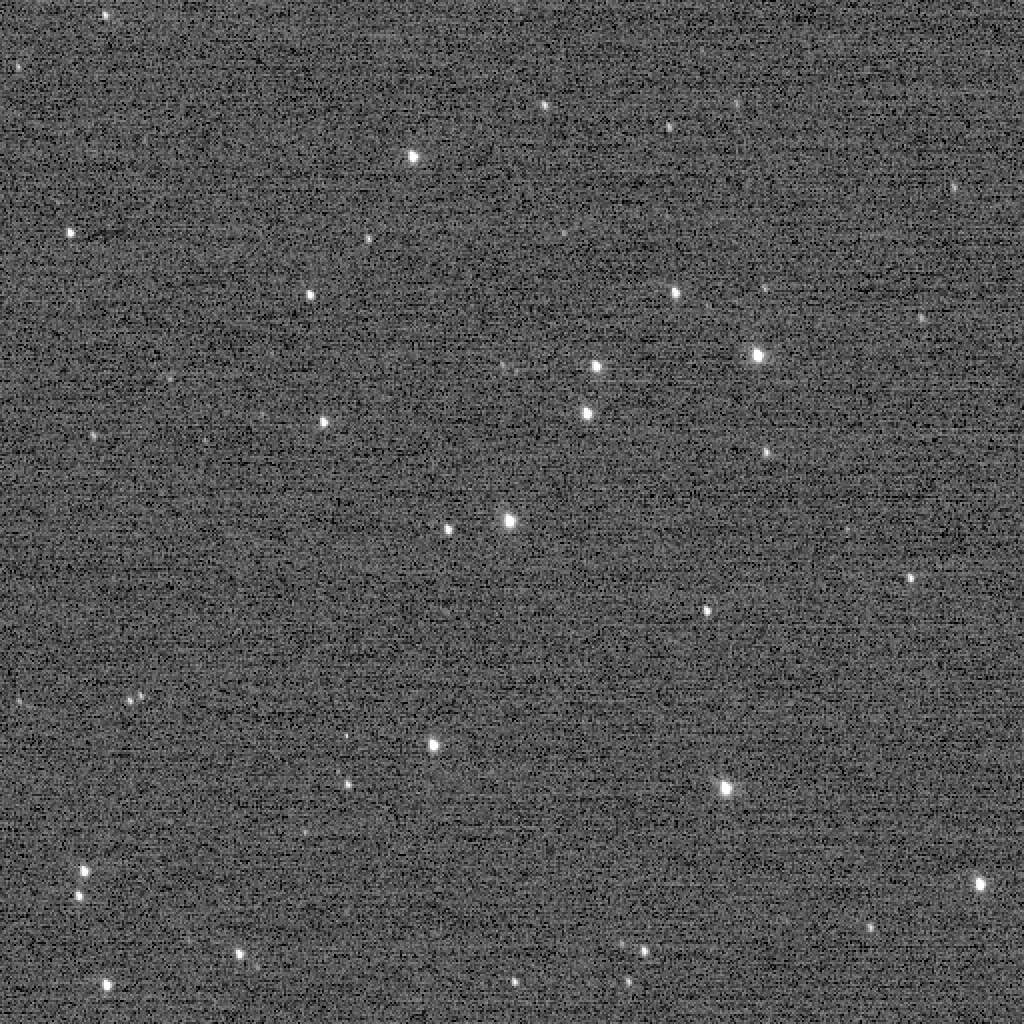

Star cluster the wishing Well cluster (NGC 3532)
From 2015 to 2016, the unit conducted a photoshoot of detailed images of the dwarf planet Pluto, thanks to which astronomers had another opportunity to explore and analyze the surface of this heavenly body in unprecedented new detail.
It should be noted that New horizons is not the first unit, which was able to get so far away from Earth. To such probes as “Voyager-1/2” and “pioneer-10/11”. However, the “New horizons” — the only man-made spacecraft, whose camera is still in working condition. At the moment the probe is in hibernation mode and moves to its primary mission objectives. Scientists expect that in 2019 the machine will be able to capture the planetoid 2014 MU69, which is located at a distance of 1.6 billion kilometers from Pluto.
Received the farthest in the history of space photography
Nikolai Khizhnyak