
Bluetooth is a technology for wireless data transmission between devices at a distance up to 100 meters. Work on the creation of Bluetooth was started in 1994 by a manufacturer of telecommunication equipment Ericsson as a wireless alternative to cables RS-232. In the result, Bluetooth was developed by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group, founded in 1998. It was composed of Ericsson, IBM, Intel, Toshiba and Nokia. Bluetooth subsequently became part of the international standard IEEE 802.15.1. The word Bluetooth is the English translation of the Danish word “Blatand” (“Bluetooth”). Nickname is the Viking king Harald I, who United the warring Danish tribes into a single Kingdom. Bluetooth essentially does the same with communications protocols, uniting them into one universal standard. How does the Bluetooth on this in today’s issue!

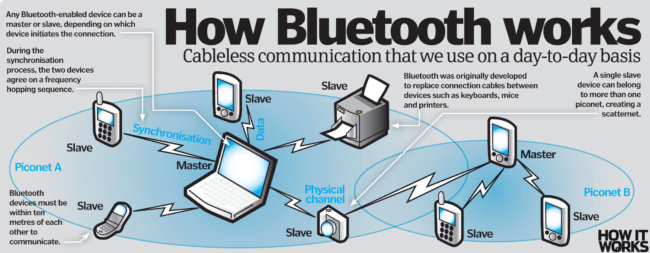
The principle of operation of Bluetooth are based on the use of radio waves. If you enable Bluetooth activates the radio transmitter which works in a limited range of frequencies around 2.4 GHz. This part of the spectrum called ISM — Industry, Science and Medicine and is used in various household appliances and wireless networks. After activation the transmitter starts monitoring all signals in this range. Second device does the same thing. After the devices found each other, the first assumes the role of transmitter, and the second is the target. With data being transmitted by a special algorithm FHSS, which provides stability to the broadband noise. According to this algorithm, the frequency of the Bluetooth signal abruptly changes 1600 times per second, jumping from one of the 79 available frequencies to another. Switching sequence between the frequencies for each connection is random and known only to the transmitter and the receiver, which every 625 microseconds synchronous rebuilt from one frequency to another. Thus, if there are multiple pairs of receivers and transmitters, they do not interfere with each other. This algorithm is also part of the system of protection of the transmitted information.

Before sending Bluetooth data is divided into special blocks, called packets, with instructions for compiling them from the source file. The processor of the receiver processes the packets, generates the transmitted file and places it in the permanent memory of the device.
When transmitting digital data and audio use different coding schemes: the audio is not repeated, and digital data in case of loss of packet information is transmitted again.
Currently the current version of Bluetooth is a specification 5.0. It was presented in London in June last year and has increased range (up to 40 meters indoors and 200 meters outdoors) and data transmission rate, component of 6.25 MB/s. Bluetooth 5.0 already supported by a number of mobile devices, particularly the iPhone 8 and iPhone H.
How does it work? | Bluetooth
Hi-News.ru