In the spring of 2012 the European space Agency and the Russian space Agency has scheduled a joint mission “Eczemas”, which consists of 2 stages: launch the Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) and sending the Rover “Pasteur”. For the last group of Russian physicists from Moscow state University and Misa has developed a miniature analyzer soil, which has already passed successfully a series of tests.
Analyzer soil is a spectropolarimeter for the study of ground stone and rocks. The uniqueness of the device lies in the fact that it has a very large set of functions and compact size. This is done due to the peculiarities of the future of the Rover. Due to the small size of the latter, the analyzer needs to be very compact, that forced scientists to go to a large number of technical and scientific tricks in order to create a sufficiently powerful small spectrometer that could identify the chemical composition of rocks by analyzing how the spectrum changes of infrared and visible wavelengths, reflected from the surface of the soil of Mars.
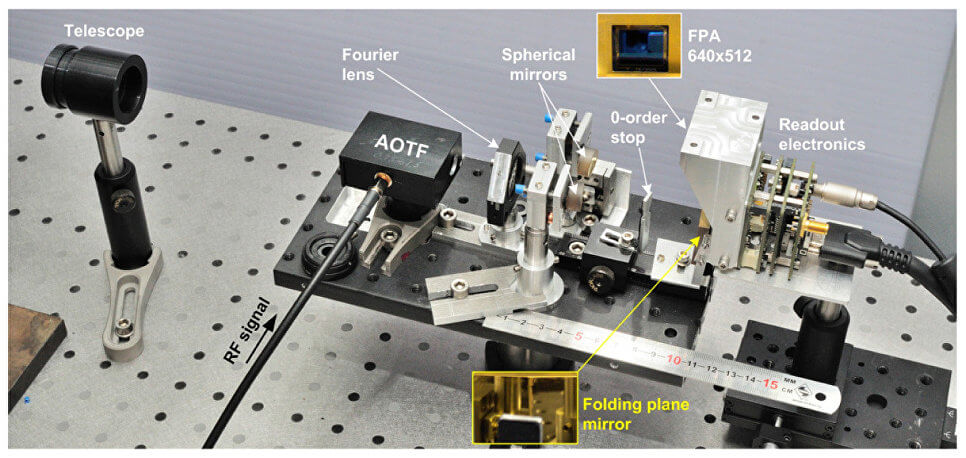
As noted in the article, published in the journal Optics Express this result was achieved with the help of new optical circuits, in which simultaneously two images in two perpendicular planes of polarization. Due to this, the spectrometer has been reduced to 10 inches in length and 20 in width at a height of only 8 inches. According to the developers, despite such a compact size, this device is not inferior to the characteristics of similar devices installed on the NASA Rovers.
Based on materials of RIA “news”
Russian scientists have created an analyzer of ground for the mission “Eczemas”
Vladimir Kuznetsov