
Since half a century ago created the National Aeronautics and space administration (NASA, NASA), it has launched hundreds of missions into space. Since the probes that touched the borders of our Solar system to manned capsules that gave impetus to the development of technology, a lot — the merit of NASA as the successor and continuer of the space race.
Here is a list of the most important and coolest NASA missions.
The WMAP satellite
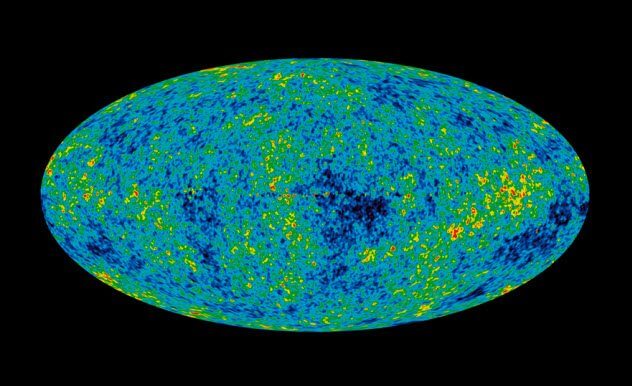
Did you know that humanity is an infant the young Universe?
We can’t get any images of the moment of the Big Bang. In the first few hundred thousand years of life, the Universe, the substance was too hot and tightly shot down, so the photons can penetrate anywhere. You can see only a few light years in any direction, before the Universe cleared a giant cloud of hydrogen is not allowed to look further.
However, after about 380,000 years, cool and spread, and the first light could escape from his prison. The light from a very tender age of the Universe falls to Earth from all parts of the sky. It shows the Universe at its early stages and is known as the radiation of the cosmic microwave background (CMB).
Since its discovery, scientists set out to map hot and cold spots CMB, to see whether they correlate with experts ‘ forecasts. Data were collected only a few decades ago. NASA had to launch a probe Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP), scientists have to get a quality radiation image in high resolution.
The results of the probe in line with expectations and confirmed that the temperature of the Universe is almost 14 billion years ago was almost uniform. It is amazing that we even managed to extract information about such distant in time and fact.
The satellite was launched on 30 June 2001 at 3:46 PM EDT time on Board the launch vehicle Delta II-7425-10. In April 2002 WMAP completed its first observation of the CMB. In February 2003 issued the first quality image of the CMB and operate the analysis of the results.
Research WMAP are among the most used and quoted in the history of space science.
The Vikings 1 and 2
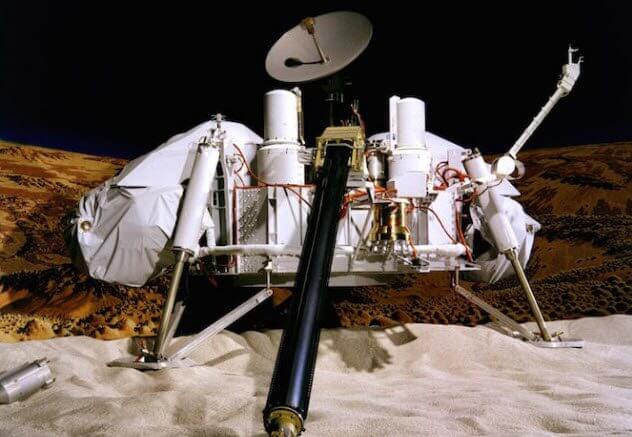
Until 1976, the US has never successfully landed a probe on another planet. Parachutes and other landing methods often did not work, and many millions of vehicles sent to the red planet, as a rule, broke the surface, moving at the speed of thousands of kilometers per hour.
To bring something into Earth orbit is often difficult. It is sometimes even harder to leave Earth orbit, go into orbit of another celestial body, and then successfully land on this planet. However, this feat of engineering was performed by probe “Viking”.
Devices-Gemini was launched during the month on rockets TitanIIIE/Centaur. Part of the transport was to remain in orbit of Mars, and the other to land on the surface.
Based on what we observed from the Earth, scientists came to the conclusion that life was not supposed to exist on Mars. But we have never been on Mars, so confidence in this conclusion there was none. When the probe sent the first images and the results of the experiments NASA, all confirmed. On Mars there was found no trace of little green men or microbial life.
Friendship 7
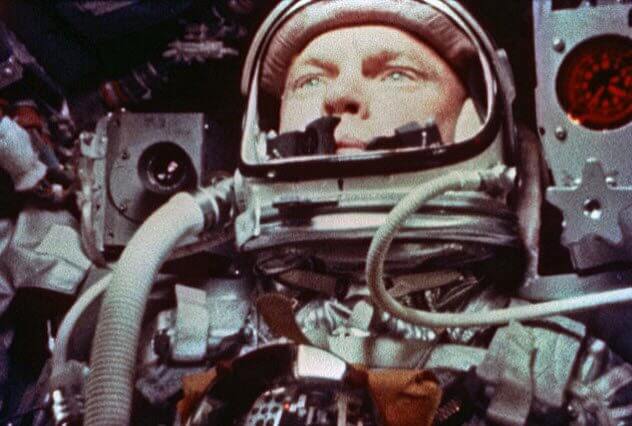

By early 1962 the United States conducted in space a little more than 30 minutes, and the clock counting down the time until the end of the decade, knocking furiously. The US sent a man into orbit, and it was critically important to get to the moon and to circumvent the Union. And that was about to change with the launch of the Friendship 7, America’s third mission to Mercury.
Colonel John Glenn, a military test pilot, had to send a new Atlas rocket into Earth orbit. The rocket soared 20 February 1962 and successfully entered the orbit of the Earth five hours. Sam Glenn successfully landed 1,300 miles South of Bermuda.
The goal of the mission is testing new missiles, to study the orbiting of the Earth and proof that man can function in space, was completed successfully.
“Gemini-IV”
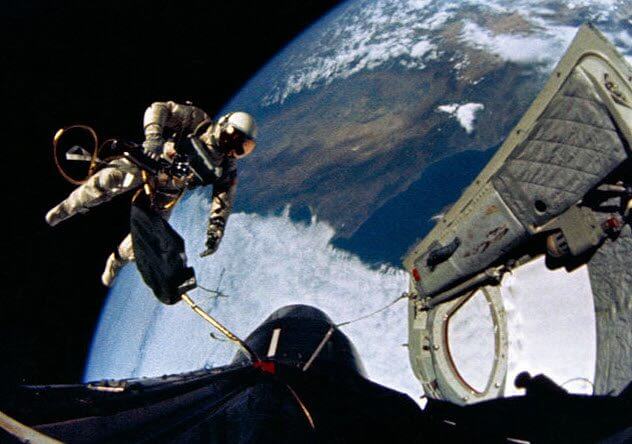

If Mercury missions taught Americans the fundamentals of motion along the orbit, the mission “Gemini” showed the equipment required for the flight to the moon. One of the most important skills on the moon was extravehicular activity or walk in space, when it was time to leave the capsule and out into the vacuum of space. And since the United States never made this before, it is extremely important to practice before stepping on the moon.
Edward white II, pilot of the U.S. air force, was to become the first American in space. Together with his friend James Macdevitt they launched 3 June 1965 on the TitanII missile. Space walk of white lasted 36 minutes and took place without incident.
The objectives of the assessment mission long-term effects of space flight (mission lasted four days) and implementation of the space walk was successful. However, the capsule landed 80 kilometers away from the target. (The astronauts forgot that the Earth revolved beneath them, when he expected the trajectory of the return).
STS-1
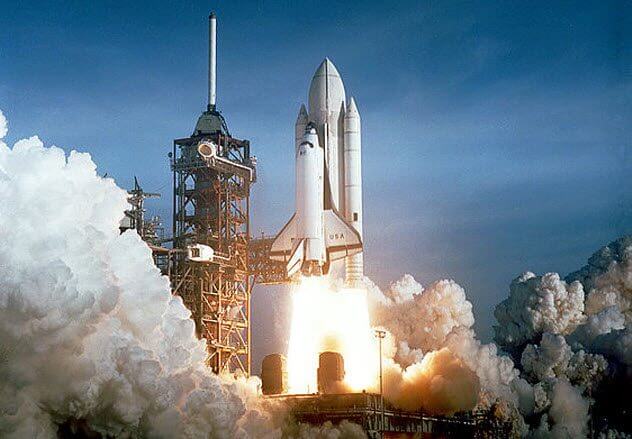

After the success of the Apollo program, NASA went in search of what would have been possible to pull off such a scale. The idea of the space Shuttle — reusable spacecraft that landed like a plane and took off like a rocket. This transport had to withdraw the experimental setup and satellites into orbit and stay in space for weeks. Planned construction of several shuttles, the first of which was Columbia.
Taking off April 12, 1981, piloted by John young and Robert Cippenham a massive rocket climbed to orbit on 166 nautical miles. The mission lasted two days and six hours, during which was checked of the ship. Then it slipped down and came in for a landing at Edwards AFB in California. At that time the Shuttle and its tank painted white, not black, white and orange flowers, which subsequently are all accustomed to.
ISS

The international space station is an important symbol of international cooperation. In the late 1990s, was delivered the first module of the station, and within ten years it was completed.
NASA space shuttles have been an important element in the construction of the station, they are taken out of astronauts and production parts from all over the world to orbit to work on the station. The first crews began to arrive in the beginning of 2000-ies. NASA also played a significant role in the research and development of details and construction methods here on Earth.
Currently, the ISS is at an altitude of over 350 km and is moving at a speed greater than 8 kilometers per second.
“Voyager” 1 and 2
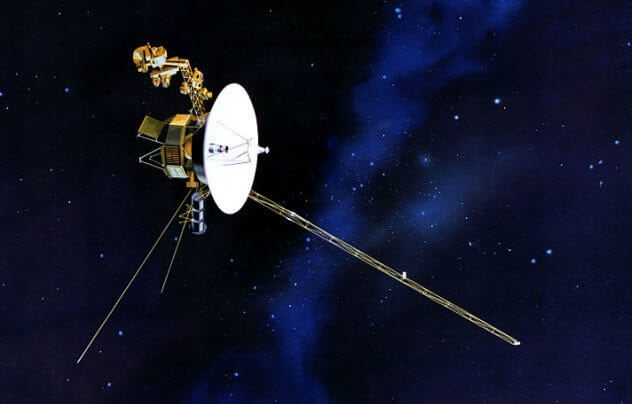

Launched in late summer 1977 on Board Titan rockets-Centaur, the probes Voyager was supposed to meet with four unexplored planets-giants of the outer Solar system: Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune and Uranus. Probes explored these planets for decades.
Currently, the “Voyager 1” is in interstellar space, “Voyager 2” in heliopause. Being at a distance of 20 billion km from Earth, “Voyager 1” is the most distant man-made object in human history.
Both tubes were provided with a message from Earth to aliens that might intercept the spacecraft, because it can survive billions of years of travel through interstellar space. All these years, the probes transmit data. But it soon stops.
“Curiosity”

Launched on the Atlas V rocket in late 2011, the Mars Rover “Curiosity” brought the most advanced (and most expensive) scientific instruments and systems ever created by engineers.
The Rover successfully landed in August 2012, thanks to an innovative system of landing. “Curiosity” was dropped by parachute. Just before landing a parachute release, and land Rover has brought rocket engines.
The goal of Rover is to repeat the success of the missions “Viking” and to determine whether there existed on Mars when conditions are suitable for microbial life. “Kyuriositi” found some evidence that Mars once could live microscopic life, but the experiments are still not completed.
“Apollo 8”

The purpose of the President Kennedy to land a man on the moon before the end of 1960-ies — not enough time. To the very end of the decade, NASA was moving at an incredibly fast pace.
“Apollo 8” was the first manned spacecraft that left Earth orbit and traveled to the moon. If he missed, he would forever remain in a cold space. If it was too close, crashed into would the moon.
The mission was sent on 21 December 1968, together with the most powerful rocket in history, the Saturn V. “Apollo-8” successfully entered the lunar orbit on the night before Christmas 1968. Stream journey was carried out on all continents of the globe.
Around the moon ten times, “Apollo-8” paved the course for his home, and successfully splashed down in the Pacific ocean on December 27.
“Apollo 11”
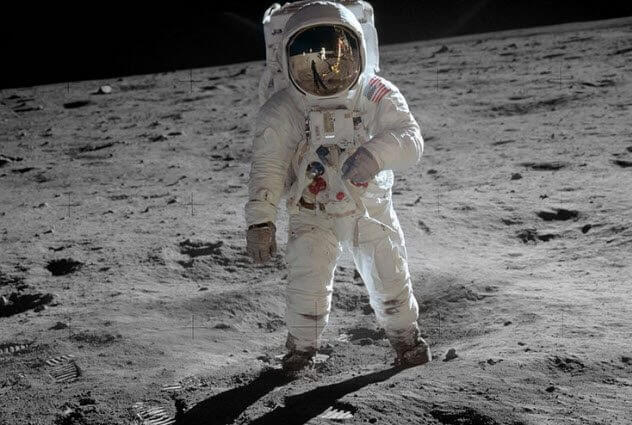

In NASA consider it a feat of human technology — the greatest of all — and difficult to disagree. Landing on the moon by “Apollo 11” in 1969, became the most famous and monumental event in the history of NASA. The beginning of the mission had on July 16, 1969. The crew was Mike Collins, buzz Aldrin and Neil Armstrong. Start and exit the lunar orbit went without a hitch, and have seen hundreds of millions of people, clinging to their TV screens.
The apparatus consisted of two parts: the command module “Columbia” which was to remain near the moon and return people home on the Earth, and “Eagle”, the lunar module, which was supposed to land on the moon. The descent took place on 20 July.
More than 500 million people on Earth watched this event on TV. The descent was difficult because the planned landing place was strewn with large stones. It was dangerous.
Using the reserves of fuel, Armstrong landed the lunar module in 6.4 kilometers from the planned place. When the engine is off and the unit sat down in the lunar dust, Armstrong uttered his famous phrase: “the eagle has landed”. (Eagle = Eagle).
Pioneers of the moon, successfully returned to Earth a few days later, laying the Foundation for five more lunar missions in the near future.
10 important missions in the history of NASA
Ilya Hel