
A new study astronomers say that about 3-4 billion years ago our Moon had an atmosphere. It was formed when under the influence of volcanic activity on our satellite solidified, and formed from this activity, the gas is accumulated so fast that eventually surrounded the moon.
The surface of our satellite is covered with impact craters filled with volcanic basalt. These basalt plains, called by astronomers the seas, formed from magma that has erupted from the bowels of the satellite to the surface, creating real lava flows. The astronauts involved in the space program “Apollo” was brought to Earth samples of lunar basalt these deposits, and their analysis, we now know that lava flows contain carbon monoxide and other gases, sulfur components, and even structural elements of water.
Now our moon has no atmosphere because it has such a powerful magnetic field and the desired ground in order to keep it. Unlike Earth, which has the right mass, and the strength of the magnetic field, able to hold an atmosphere, any atmosphere generated around the moon will be quickly blown away by solar winds. But a new study indicates that the Moon could really be the atmosphere before happened like this.
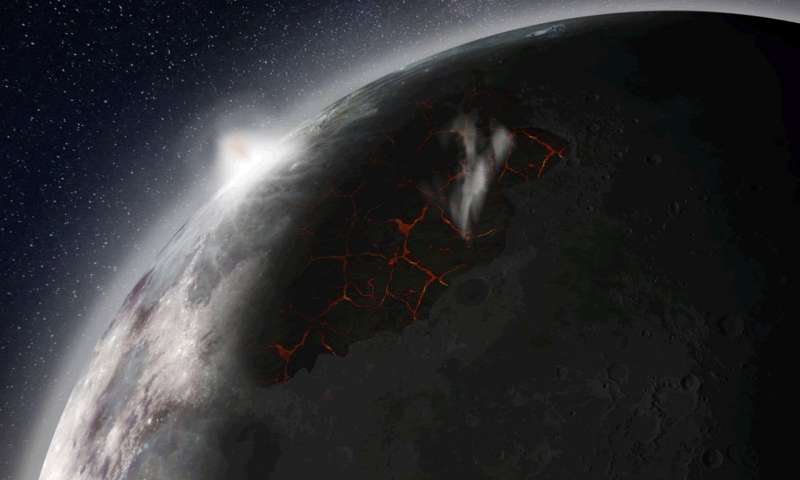
A team of scientists examined the samples and found out how much gas was to appear and accumulate, in order to form around the moon such a transient atmosphere. It turned out that the peak of volcanic activity on the moon occurred about 3.5 billion years ago, when the atmosphere of the satellite had very dense form. After its formation, it existed about 70 million years, after which they were discarded and lost in space. During the period when the Moon had an atmosphere, the satellite was almost three times closer to the Earth than now, and much bigger than looked in the night sky of our planet.
“The results of this work are forced to significantly change our view of the moon as airless, lifeless piece of space stone, as once our companion was surrounded by an atmosphere, and is more dense than has, for example, the current Mars,” commented a senior researcher of the space research Association universities David Kring portal Phys.org.
New the obtained data are important for future astronauts who plan to participate in lunar missions and subsequent space exploration. Scientists suggest that the composite volatile components of the ancient atmosphere of the moon could be preserved closer to the pole of the satellite, as well as in cold, permanently shaded areas. If so, then on the moon right now, there may be a source of ice future astronauts and colonists will be able to use for the production of drinking water, growing food, and other needs. Deposits of ice in combination with their chemical elements can also be used for the production of fuel and air as the ground for lunar operations and outside of the satellite, which is planned to turn into a platform for future space missions and flights into deep space. In addition, the presence of any useful object on the moon will mean that it will not have to carry from Earth – huge advantage, especially when you consider how expensive it is shipping the payloads to space.
The ancient Moon had an atmosphere
Nikolai Khizhnyak