
The effects of human presence on Earth has been worsening with each passing day. Our energy consumption is growing and getting worse. The population is also growing, which creates a serious shortage of space, water and food. Finally, rapidly changing environment, and nature has a profound impact on cities around the world. To address some of these challenges required innovative changes in the field of old building technologies that will make future beautiful, clean and, most importantly, livable.
Bamboo town

Most modern people think of bamboo decorative material. But really it’s an incredible building resource. Bamboo grows quickly, it is stronger than steel and more resistant cement. Therefore, Penda, architecture Studio in Beijing, China, wants to use bamboo as the main resource for the construction of an entire city.
This city will be a sustainable, environmentally friendly and inexpensive. The building will be built, tying together bundles of bamboo, tying up their rope. Using this technique, Penda thinks they can build a city that will accommodate 200,000 people by the year 2023.
Once the overall structure is completed, it will be possible to easily add horizontal and vertical blocks. In addition, a room or even a whole building made of bamboo can be dismantled without much effort, and bamboo rods can always be reused.
Diamond nanowires

As far as we know, diamonds are the most durable mineral that occurs naturally on Earth. This makes diamond a perfect material for construction with the proper approach.
Scientists at the University of Pennsylvania have created innovative diamond nanowires, which are 20 000 times thinner than a human hair. This diamond nanowires are considered to be the most durable material on Earth (and possibly in the entire Universe). In addition to the subtlety and strength, they are also incredibly lightweight.
The researchers were able to create these threads ultra-thin diamonds using alternating cycles of pressure to isolated molecules benzene in the liquid state. As a result, were born rings of carbon atoms that were sequenced in the circuit.
Such nanowires may, are unlikely to use in everyday construction, but in ambitious projects, for example, when a tether of a space Elevator, quite.
Aeroginosa insulation

Aerogel is not new material. It was discovered in the 1920-ies. It is created in the process of removing liquid from gel and replacing liquid gas. In the process, the substance becomes ultra-light, because 90% of the air. To isolate it fits perfectly. The aerogel used for insulation of pipelines in industrial zones and even on the Rover.
Aspen Aerogels wants to use aerogels for home insulation. The company has created a product called Spaceloft blankets, which is quite simple to operate because of their weight and fineness. Despite their lightness, these blankets are two to four times higher than insulating properties in traditional insulation of fiberglass or foam.
Spaceloft blankets also allow water vapor to pass through them, and are fire resistant, oddly enough. Although the house, wrapped the aerogel will not be as fire resistant as home in “451 degrees Fahrenheit”, this type of insulation should reduce the number of home fires.
The problem is that the aerogel is much more expensive than traditional insulation, though it will save money on energy bills in the long run. In addition, not all homes can easily upgrade this material. These blankets are best suited for old houses or new ones, which will be specially arranged to isolate the aerogel.
Road printer

Building roads takes time. On average, a single worker can lay 100 square meters per day using traditional methods. Road printers like Tiger Stone can shorten this process by “printing” to 300 square meters of cobblestones per day.
Another RoadPrinter RPS can lay up to 500 square meters per day. One to three operators fed bricks machine. A pusher sorts the bricks in a pattern like a carpet. At this point gravity takes over and the machine lays brick road. Then, similar to the rink the roller presses down the bricks to the place.
These printers run on electricity and do not contain many moving parts, making them easy to use and maintain. In addition, they don’t make much noise, especially compared to traditional methods of paving roads.
Of course, the main difference between most of the roads and those that placed these printing machines, in that they lay bricks, cobblestone or tile instead of asphalt. However expensive block even better than asphalt, because they filter the water, expand when frozen and will last longer.
Bestrasova multi-directional lifts
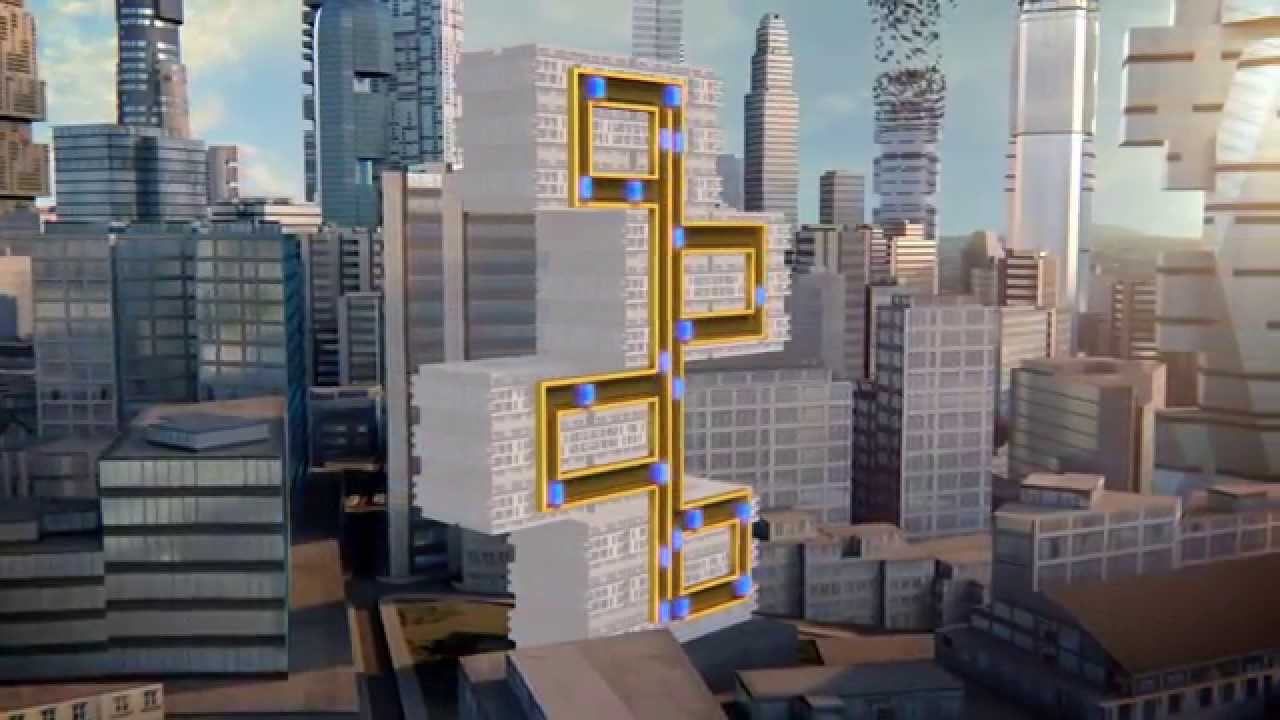
A big problem with large infrastructure is that there is no efficient way to navigate. People always go with the same speed and at a certain distance. And every Elevator is often only one moving Cabinet. If you had to use the Elevator in a big building, you know that sometimes waiting is like death.
German manufacturer ThyssenKrupp elevators plans to get rid of these problems. Instead of using the cables he proposes to put the elevators on the basis of magnetic levitation (Maglev trains). Then they will be able to move both vertically and horizontally. It will also allow you to use more than one cabin to the mine, saving the waiting time.
Finally, magnetic elevators will consume less energy, which is also good for the environment. In 2016, ThyssenKrupp plans to test a new Elevator system in the building at their research campus.
Solar paint

One of the most common complaints about solar panels is that they are large, sort of an eyesore, and not powerful enough. To change this, several researchers are working on solar cells that are so small and flexible that they can be paint on the surface. In fact, the team of researchers from the University of Alberta have created solar cells by spray with nanoparticles of zinc and phosphorus.
If every homeowner will paint your roof like solar paint, we can produce more than enough energy for the house, thus reducing the dependence on fossil fuels. In addition, the solar paint is cheaper to manufacture than traditional solar panels. Solar panels used in this paint, while not very efficient, but scientists are working on this problem.
Vertical city

According to forecasts of the United Nations, by 2050 the Earth will be more than 9.6 billion people. That’s 2.3 billion more goals than we have today. In addition, it is assumed that 75% of the world’s population will live in cities, which will exacerbate our problems with lack of space in these cities.
One way to solve this problem is to build a vertical city. There are already several proposals for vertical cities that can be built in the Sahara, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and China.
These vertical cities will be giant buildings, which will provide people with houses, jobs and shops. For example, Italian firm Luca Curci Architects plans to build 189-storey building in the UAE. It can accommodate 25,000 people with shops and offices. Because people will not need to leave the building, it will solve the problem of space and reduce carbon emissions.
Such megastone will be self-sustaining and green. Because they are large, total area of walls can accommodate solar panels. They will also use geothermal energy and collect rainwater.
Smart concrete
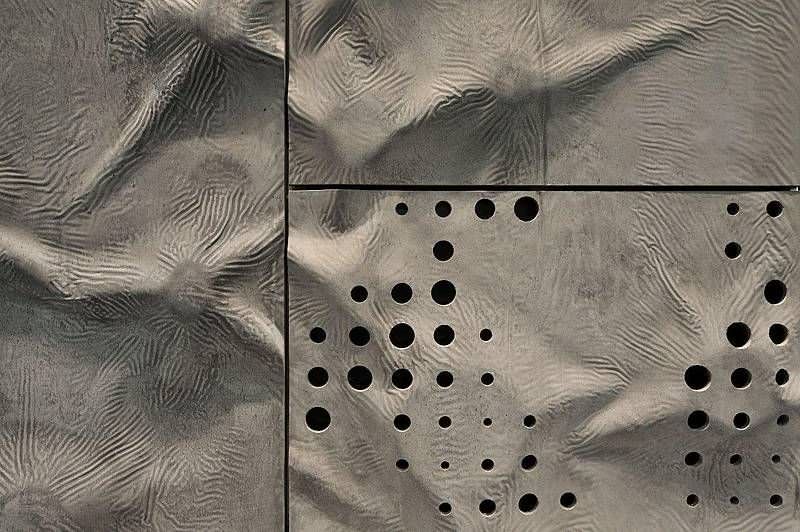
When the area begins to flood, the water has nowhere to drain. In the city is worse because there is less soil to absorb water. To reduce the threat of flooding, a British company Tarmac have created an asphalt called Topmix Permeable.
Most types of concrete allows water to soak into the ground, but only 300 mm per hour. Topmix allows you to skip 36 000 millimeters of water per hour, and it is about 3300 liters per minute.
Instead of using sand for concrete, Topmix includes pieces of granite crushed stone, Packed together. Water seeps through these pieces of granite, and once absorbed into soil, flows away into the sewer or collected in a water reserve. In addition to reducing the chance of flooding, Topmix can keep the streets safe and dry. In addition, water can be directed into tanks and used for the needs.
The problem of permeable concrete in that it can be used only in places where are not too cold. Cold weather will lead to expansion of concrete, which will destroy it. It will also be more expensive than conventional concrete, but long-distance the city can save money by reducing flooding.
Smart bricks
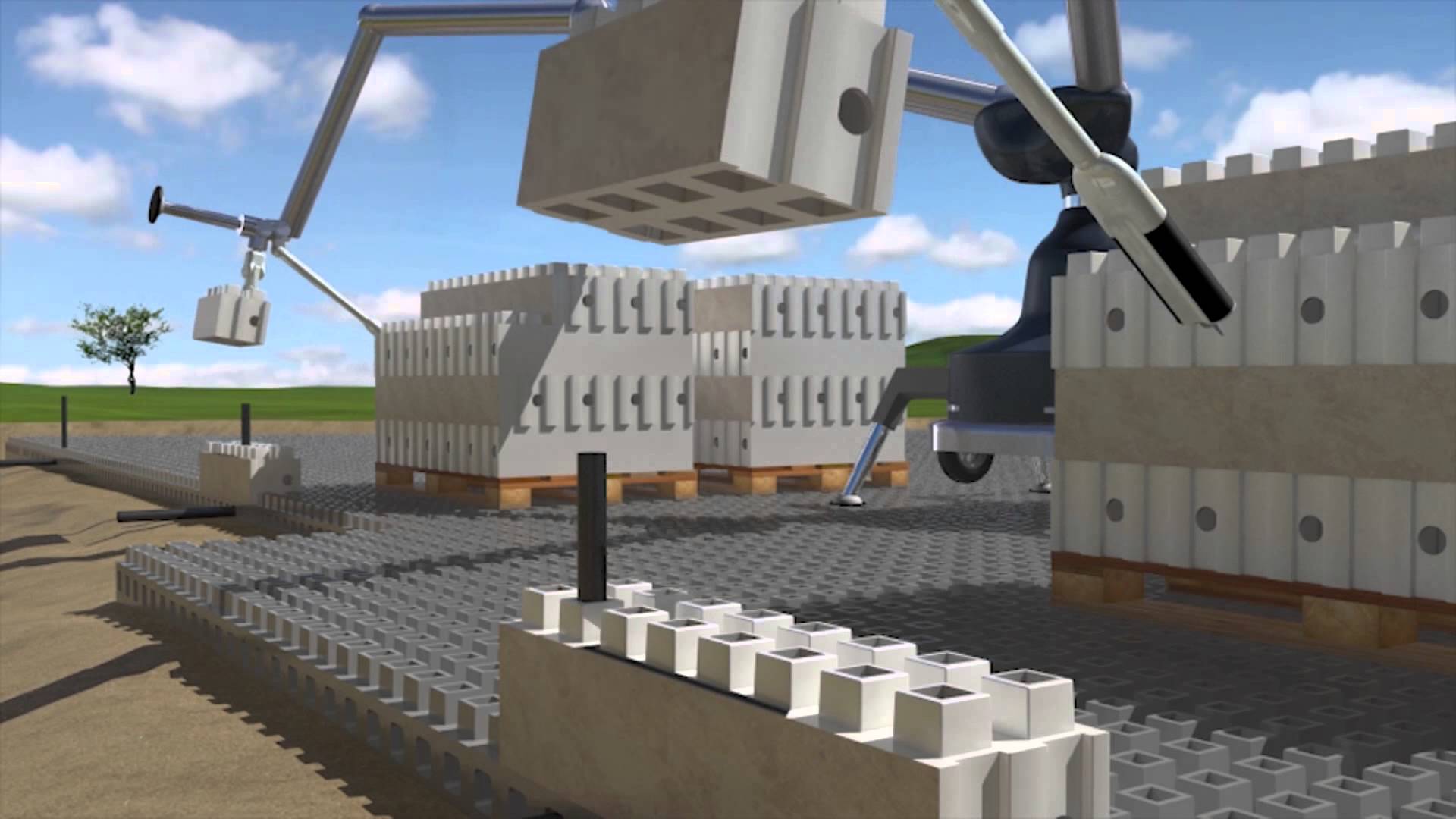

Looking at the development of Smart Bricks, Kite Bricks, it is easy to see their resemblance to Lego bricks. These building bricks have handles at the top and can be connected like Lego pieces. Smart bricks are held in place using reinforcement and come in many different forms.
Instead of using cement, these bricks are fastened together in a strong double-sided adhesive. From inside the building to the bricks you can attach removable interchangeable panels. These panels can be removed if necessary. There are also cubes for building floors and ceilings. In the center of the blocks are empty, they can fill in when needed insulation, pipes and wiring.
These bricks can lead to improved heat control, flexibility in manufacturing and reduce the cost of production by 50%.
Swarm construction robots

In search of innovative methods of construction, Harvard researchers turned to nature for inspiration, in particular to termites. Termites can build large structures in the absence of Central control. To this end, they are just a piece of dirt on the first construction site. If she’s busy, carrying to the next place.
The TERMES project uses the same idea of swarm construction, but uses small robots. These simple, low-cost drones are building a structure, following the original design and laying out the blocks in the first available place until the structure is complete. Roy doesn’t need human intervention after the initial tasks.
This rod would be perfect for building structures in dangerous locations, in space or under water. He could also do menial jobs, saving people’s time.
