Scientists of the Department of cell and molecular biology, University of California at Berkeley using the method cryoelectron microscopy received the most detailed to date picture of the structure of human telomerase – an enzyme that ensures the immortality of cells. The results of the work done and the intricacies of the structure of the enzyme, the researchers shared in the journal Nature.
To begin the synthesis of new chain to the mechanism of DNA replication requires the presence of a short matrix, which is then destroyed. In the process, at the end of each chromosome remain nedropolzovanie short pieces that with each round of replication continue to shorten. Keep the important parts of the chromosome from the terminal naturalisatie help telomeres — region at ends of chromosomes, composed of repetitive sequences and which are essentially “back-up” DNA. Telomere length limits the number of cell divisions a particular value (limit of Hayflick). Cell lines telomere length is maintained at a constant level telomerase the enzyme that maintains chromosome ends and prevents them from fraying, which in turn leads to aging of the cells of the body, says phys.org.
Because telomerase is also involved in the processes of carcinogenesis (formation of tumors), it is of great interest to scientists as a starting point for the development of cancer therapy, substances that inhibit its activity, will be able to stop tumor growth. However, to develop effective inhibitors of the enzyme necessary to present its structure. General plan of the structure of the telomerase has been studied relatively well. At the moment the best structure with a resolution of nine Angstrom was obtained for the telomerase of the ciliate Tetrahymena. But, of course, the main interest for physicians is the structure of the human enzyme. And just here there is a lack of sufficient quality data about its structure.
With the help of technology cryoelectron microscopy, researchers from the University of California at Berkeley under the direction of Kathleen Collins received images of human telomerase, is associated with the substrate, subnanometre resolution 7.7 and 8.2 Angstrom.
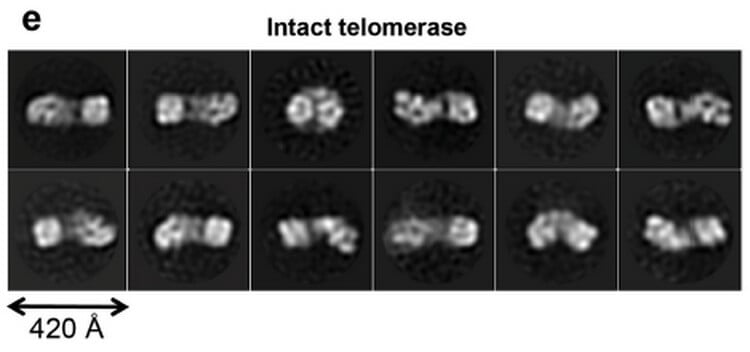
The raw image of particles of telomerase
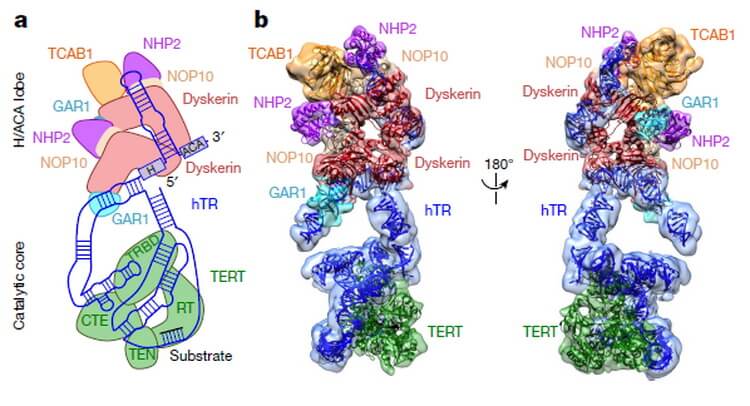
The detailed structure of the telomerase
In identifying the structure still lacks a little detail, but in combination with knowledge of the gene sequence of human telomerase it provides enough information to start thinking about potential drugs that will help slow down aging and cure cancer.
Scientists have considered the enzyme to cell immortality
Nikolai Khizhnyak