A lot of pictures of Pluto don’t exist. The NASA probe New horizons passed a new package of images that show we spotted the plain surface of a Satellite in an unusually high resolution.
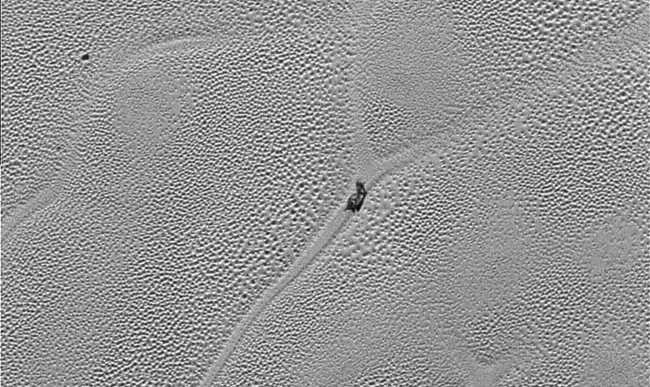
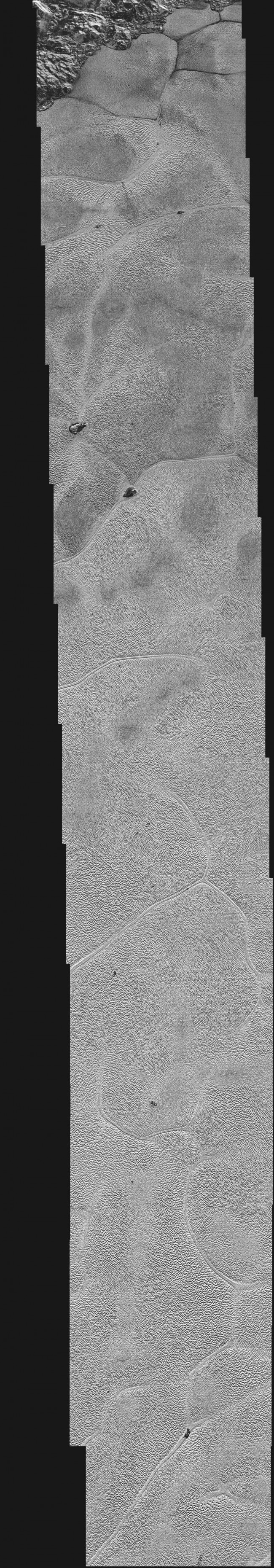
Polygonal fossa, prominent in the pictures, have a diameter of from 16 to 25 kilometers and a depth of 90 meters. Scientists believe that these patterns arise from the melting of nitrogen ice under the surface of the dwarf planet. Warmer material rises, then cools and sinks down again.
“This part of the Pluto acts like a lava lamp,” says one member of the team “New horizons,” William McKinnon.
Large dark boulders are prominent in the photograph, consisting of scientists believe dirty water icebergs.
A team of researchers has combined several images into one to show the 650-kilometer stretch of plains Satellite. The image resolution is about 80 meters per pixel.
The researchers also received a color photo of the region, located to the West of the plain Companion and bears the informal name of the Land of the Viking. On the photo you can see the rims of craters and the area covered by the red dust.
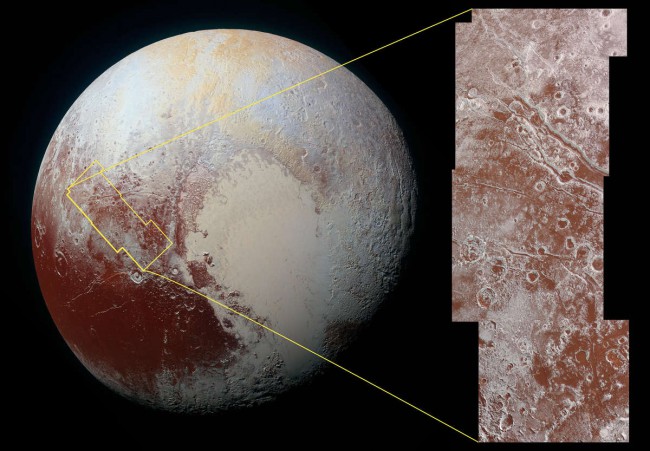

Red color caused by the presence of molecules of tolinou that arise in the interaction of methane and nitrogen from the atmosphere of Pluto with the solar light. Tolini are organic substances and are considered to be chemical precursors of life. In addition to Pluto, tolini are also found on Titan, Triton and other moons, and comets of the Solar system.
According to the materials of Popular Science
