
In the last issue we talked about how the LCD display. Today we will focus on a different technology, called OLED. So, how does the display on the organic light emitting semiconductors — this is in the news today!

The main difference between OLED-display from LCD is that in the second case, the pixels are lit, and in OLED emit their own light. The brightness of the OLED display can be controlled pixel by pixel.

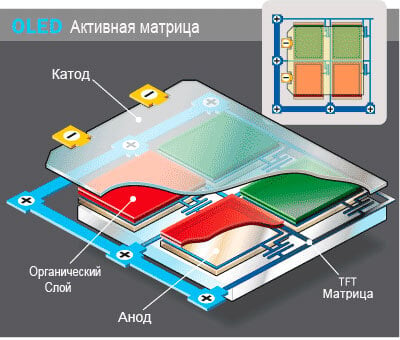
OLED display consists of several very thin organic films between two conductors. Supply a small voltage to these wires (from 2 to 8 volts) and causes the display to emit light and, consequently, display images. To create an organic led uses thin-film structure consisting of layers of several polymers. One of them is called equity, as it there are processes leading to the emission of light waves. And the other layer is called conductive. To control each pixel of the OLED display, you need each of them to bring the control voltage. When voltage is applied in layers starts the movement of electrons. In the emission layer changes the energy of the electrons when meeting with other charges, and there is radiation in the area of the visible spectrum waves.
In an active matrix for controlling the pixels are used thin-film transistors, which are arranged in a matrix, as in LCD displays. Feeding control signals to the individual transistors, to manage a particular pixel.
There are three schemes of color OLED displays. The most common option and the most efficient use of energy is a standard three-color model, referred to as the model with separate emitters. The three organic materials emit light in primary colours – red, green and blue.
The second option is to use three identical white emitters that emit light through color filters, however, this model loses the first option for efficient use of energy.
In the third case applies blue emitters and special fluorescent materials to convert short-wave blue light into longer wavelengths – red and green.
In all embodiments, OLED displays provide good color reproduction, high contrast and brightness, have a smaller weight and dimensions compared to LCD displays. Of the benefits you can also select a low power consumption which is directly proportional to the brightness and the luminescence area. OLED displays no screen burn with prolonged display of static images. In addition, the image can be clearly seen from any angle (180 degrees).

On the downside, the main problem with OLED displays is the short lifetime of the diodes of certain colors, which is about 2-3 years. This is especially true of blue. But if you use only white LEDs, their lifespan reaches 100,000 hours. Another drawback of OLED displays is the high cost.
It is expected that the change in OLED displays can come more effective and efficient TMOS display (optical shutter TDM). This technology uses the inertia of the retina of the human eye. Also are working on Organic TFT displays — working technology of organic transistors.
How does it work? | OLED display
Hi-News.ru