The French team of engineers, Institute Femto-ST in besançon (France) invented and constructed a new system of microscopic robots, which greatly expanded the boundaries of optical nanotechnology. Making combination of several already existing developments, the “factory” μRobotex nanobots could build complex microstructures in a vacuum chamber, then fixed them on the tips of optical fibers with nanometer precision.
Still technology Lab-on-fiber had robotic actuators for nunobiki, so the work at this scale prevented the engineers to create the microstructure. Now miniature sensing elements can be mounted on the tips of optical fibers that allows you to see the micro-processes and manipulate with high precision. The application of this technology is very wide: since the fibers thinner than a human hair, they can penetrate the blood vessels for optical detection of bacteria and viruses, as well as, for example, can be used for the precise calibration of the spacecraft of the future.
To test the effectiveness of new technology decided a team of French materials scientists under the leadership of Joel Angus from the University of Burgundy — Franche-comté. They used a system μROBOTEX consisting of a scanning electron microscope with a large chamber in which are arranged unit with the focused ion beam, gas injection system and a micromanipulator with six degrees of freedom.
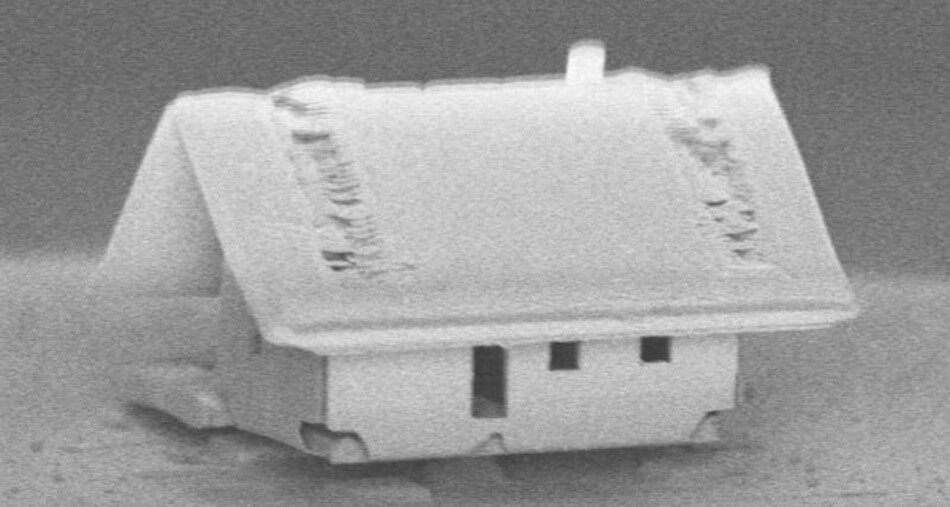
Using the system, scientists have created a miniature model of a house with a length of about 25 micrometers. To this end, the silicon sheet was cut reamer of the house, after the walls themselves are gathered from a flat sheet into a unitary structure by bending under the action of irradiation by ions, say the authors in the journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A.
To create a house using these tools, the researchers took silicon wafer having a thickness of 1.2 micrometer. Using ion beam to carve the pattern of a house with four walls in which the same method cut the Windows and door. Then, using a technique resembling the technique of origami, the authors have collected the vast walls of the flat pattern. Instead of bends in a sheet of paper scientists have thin joints between the base and each wall using the ion irradiation of gallium.
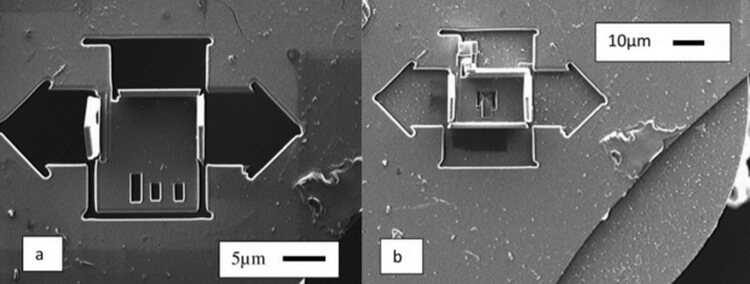
The Assembly of the walls of the house
The principle of the Assembly of this “origami” based on the fact that at a certain for each material thickness, he begins to spontaneously bend from the radiation. This is due to the fact that gallium ions penetrate into the sample and mostly heat the lower part of the plate. In result it formed two zones — hot and cold — which expand with different intensity. This leads to the fact that the plate is bent in the place of refinement, and the walls raised to the desired position from a flat template.
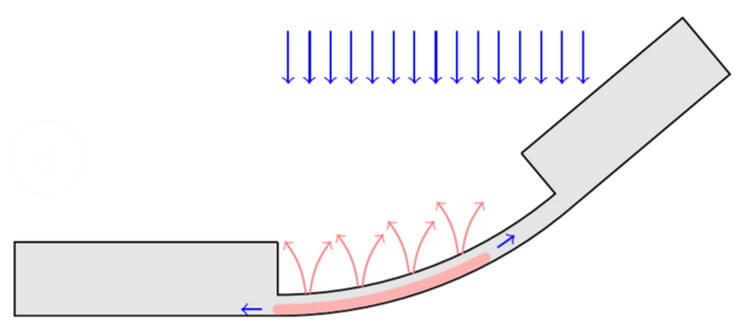
The principle of bending of a plate by irradiation with ions
Then Dom welded at the seams by the end of the optical fiber by using gas spraying. Then, from a silicon wafer similar to the walls cut the two parts of the roof that is brought to the house with a micromanipulator and welded coating. The researchers also attached to one of the roof slopes pipe and the result was a miniature house with a size of about 25 micrometers on the tip of the optical fiber.
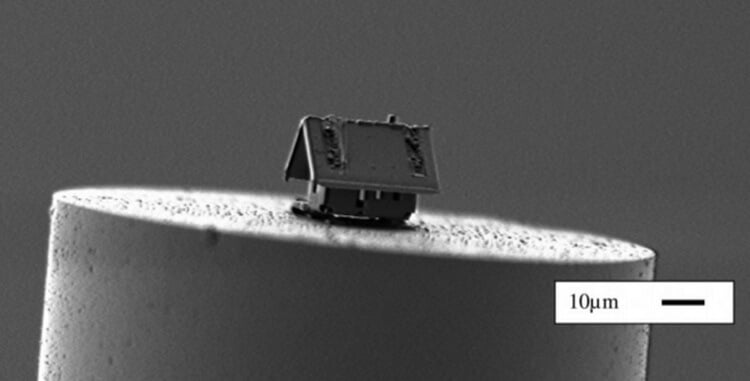
House at the end of the fiber optic
French engineers constructed the world’s smallest house
Nikolai Khizhnyak