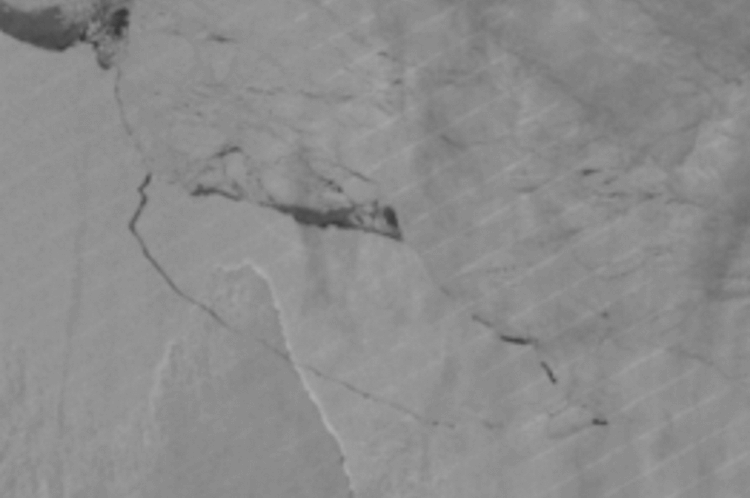

In the photo above don’t say it, but there is no mistake. From Antarctica just broke off one of the largest ever recorded iceberg, half the size of the area of the island of Jamaica. The cause was a crack appeared in the ice shelf of Larsen C. a Clear rift in the glacier emerged in 2010 and since then began to grow rapidly. In the period from 10 to 12 July this year, the process of separation ended. As a result, the light appeared one of the largest recorded by the science of icebergs, whose area is 5800 square kilometers.
“Hot news! From the Larsen shelf was separated by a giant iceberg. Soon there will be details,” — said on his page on “Twitter” a geologist at the University of Swansea Martin Oliri early in the morning this Wednesday and immediately showed some satellite images of the MODIS unit.
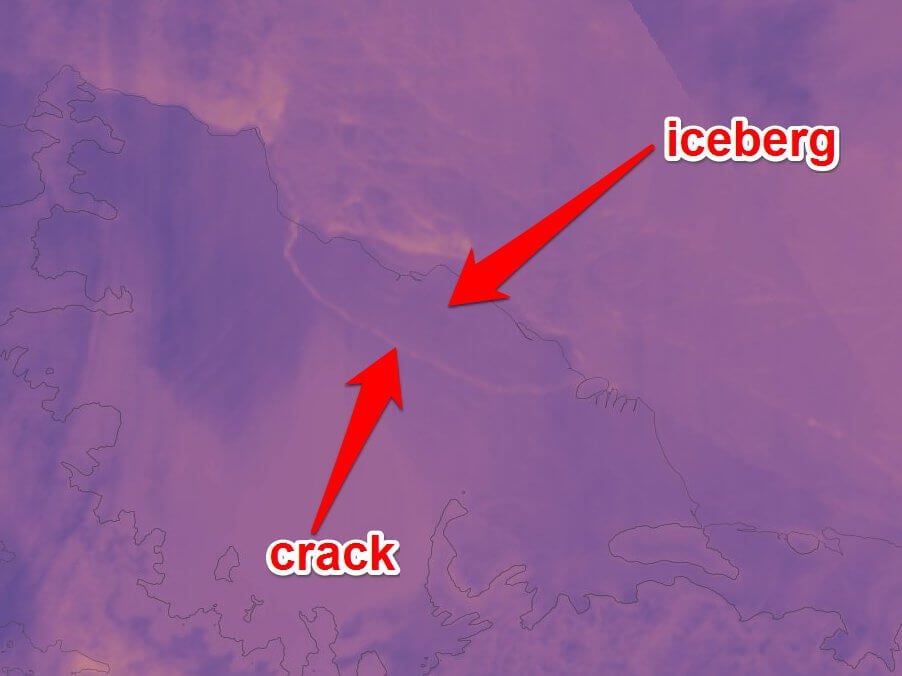
Earth probe NASA MODIS one of the first took a picture of the breakaway from the Antarctic giant piece of ice. However, judging by the image above and the image provided by lednikovogo Adrian Luckman (see below) from the same University in Swansea, it seems, the breakaway piece remains stationary.
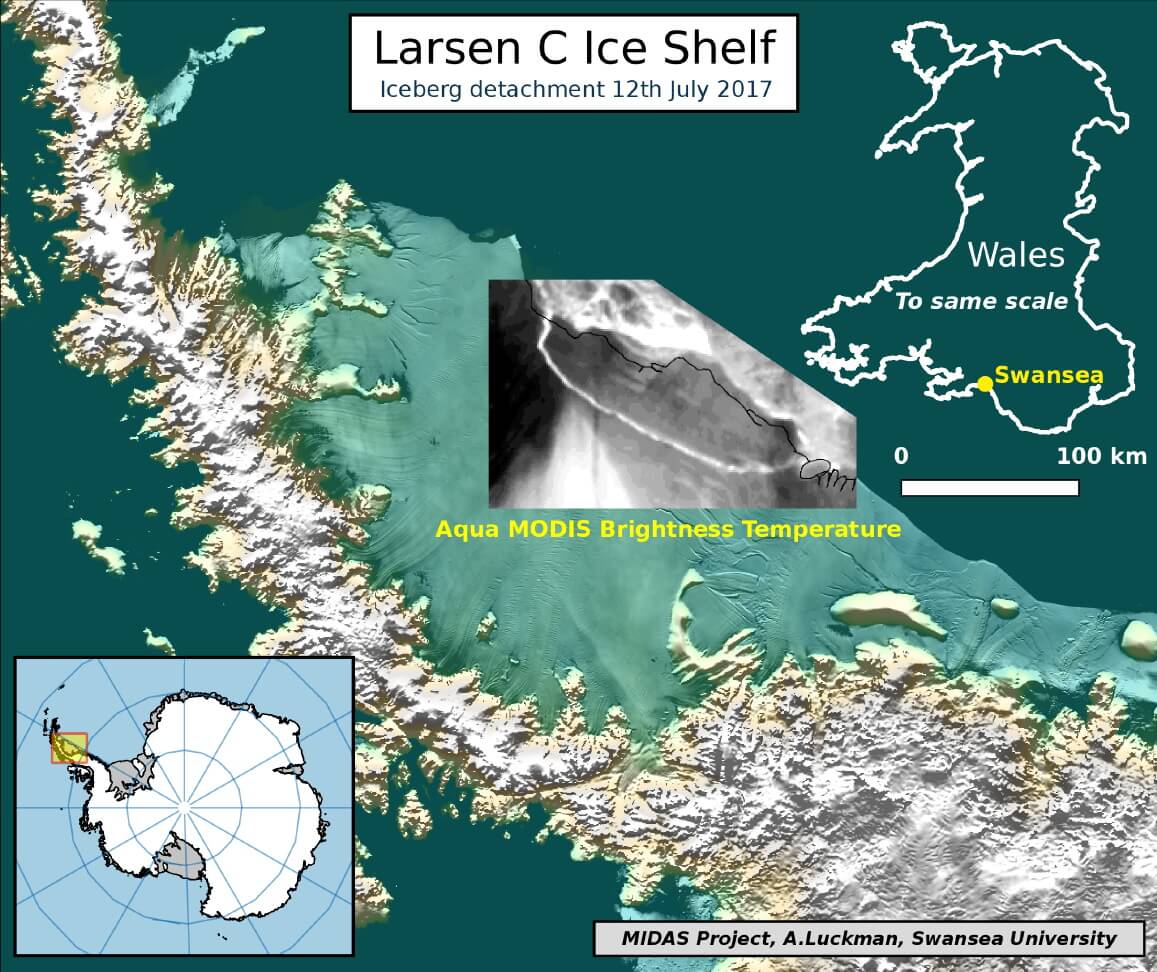
According to available satellite imagery and information provided in the “Twitter” The Antarctic Report of 6 July, this may be the third biggest ever breakaway iceberg. According to Luckman and Oliri, “the mass of one of the largest icebergs, which are likely to get labeled A68, may be around 1 trillion tons.”
“This iceberg is 12 percent of the total area of ice shelf the S. Larsena appearance of the Antarctic Peninsula changed forever,” said the scientists.
A few days before he broke away from the shelf, a geologist at the University of Edinburgh Noel Harmelen and his colleagues calculated that the thickness of the iceberg, which will now drift through the glacial southern ocean, is 190 meters and it consists of approximately 1155 cubic kilometers of frozen water. This will be enough to fill to the top with ice 460 million Olympic swimming pools, or roughly all U.S. lake Michigan is one of the largest natural pools of fresh water in the world.
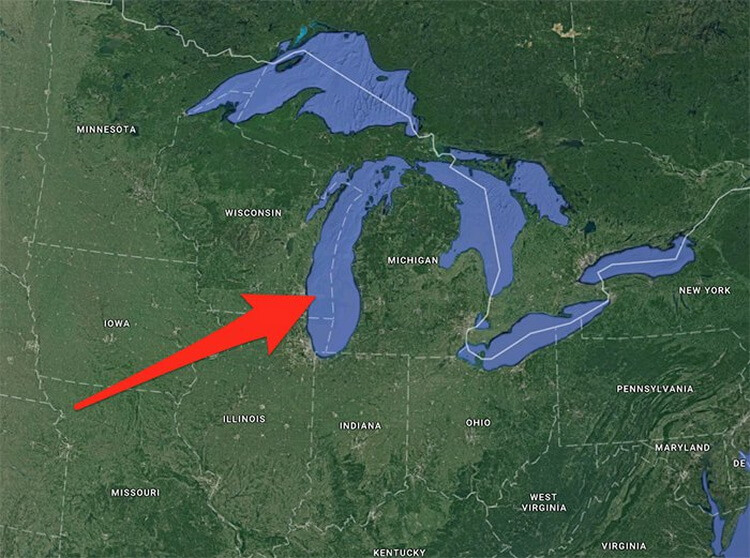
Lake Michigan for comparison
Scientists still can’t accurately predict what will happen next, as the icebergs of this size break away infrequently.
“It can, for example, continue to understand. In whole or in part it can get to the North, the ocean currents and carry down to the Falkland Islands,” suggests Anna Hogg, lednikoviy Leeds University.
By the way, these Islands are located more than 1600 kilometers from shelf Larsen.
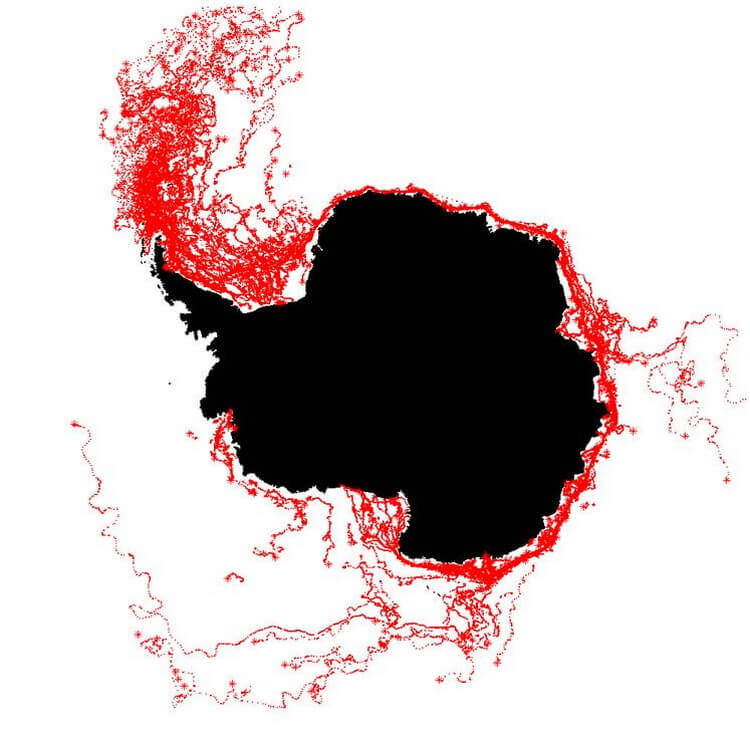
The illustration below shows the path of movement of hundreds of icebergs in the period from 1999 to 2010.
Himself ice shelf Larsen is one of the largest ice shelves of the Antarctic continent. As representatives of project MIDAS, “a large part of the shelf consists of fallen in the last few hundred years of snow, but the inner layers of the glacier are much older.” In early June, the scientists of this project reported on the receipt of satellite images where you can find the fault. It has a North direction and goes to the side of the southern ocean.
According to some researchers, if (or when) the entire shelf, Larsen C, and the accompanying glaciers melted, the sea level may rise by 10 centimeters. However, experts on Antarctic studies say that this event is unlikely, and in General call the appearance of icebergs, even of this size, though impressive, but quite logical and natural process.
“The appearance of giant icebergs, like this is a normal part of healthy behavior of the ice crust that were formed over decades, centuries or even for millennia,” comments Helen Amanda Fricker, lednikoviy from the Institute of Oceanography SCRIPPS name.
“That seems incredible, in fact, is common practice in this part of the Antarctic”.
However, Fricker notes that such natural processes are accelerated significantly the global climate changes mainly caused by human activity.
“In General there is an acceleration of the processes of change in Arctic reservoirs and the loss of mass in key areas of the Antarctic. Continuing this weight loss sooner or later lead to irreparable events.”
From Antarctica broke off a piece with a mass of 1 trillion tons
Nikolai Khizhnyak